Introduction
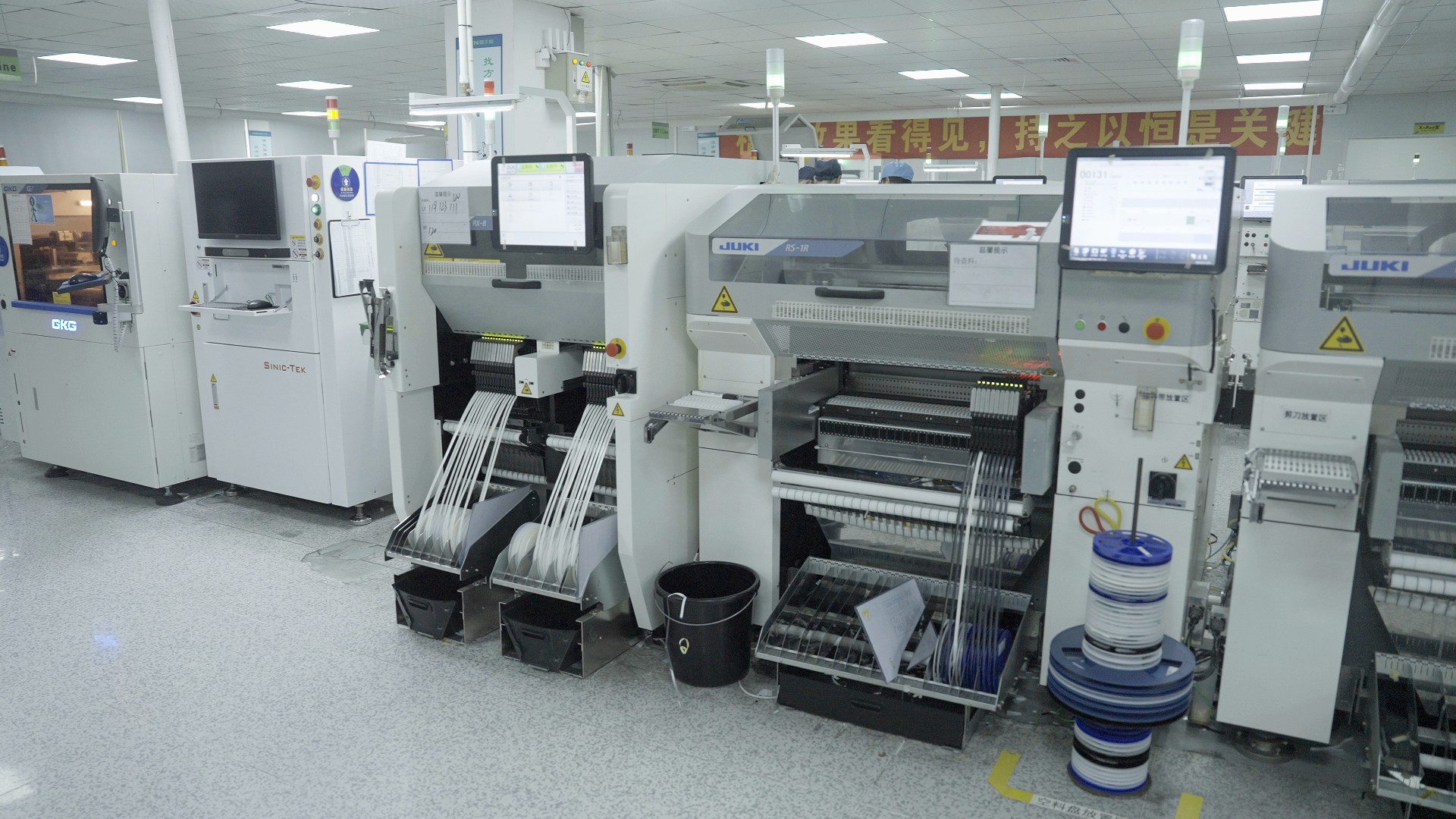

In the fast-paced world of electronics, surface mount technology (SMT) has emerged as a crucial player in manufacturing efficiency and product miniaturization. The rise of SMT machines has transformed how electronic components are assembled, enabling faster production times and greater design flexibility. As we delve deeper into the intricacies of what is the SMT used for, we uncover its pivotal role across various industries, from consumer electronics to medical devices.
Understanding Surface Mount Technology
Surface mount technology is a method where components are mounted directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs), eliminating the need for traditional through-hole mounting techniques. This innovative approach allows for more compact designs and higher component density, making it a favorite among engineers and manufacturers alike. By understanding what does surface mount mean in practical terms, one can appreciate how this technology revolutionizes modern electronics.
The Growing Importance of SMT Machines
The demand for SMT machines has surged alongside the growing complexity of electronic devices and consumer expectations for performance. These machines are not just tools; they represent an evolution in manufacturing processes that enhance speed and precision while reducing costs. As we explore the question, what is the difference between SMT and SMD?, it's essential to recognize that these advancements are driving industries to adopt SMT technology at an unprecedented rate.
Applications of SMT in Modern Electronics
From smartphones to automotive systems, surface mount systems have found applications across a vast array of products that define our daily lives. The versatility of SMT enables manufacturers to create smaller, lighter devices without compromising functionality or reliability. By investigating what is the SMT used for in these contexts, we can see its undeniable impact on innovation and efficiency within modern electronics.
What is Surface Mount Technology?
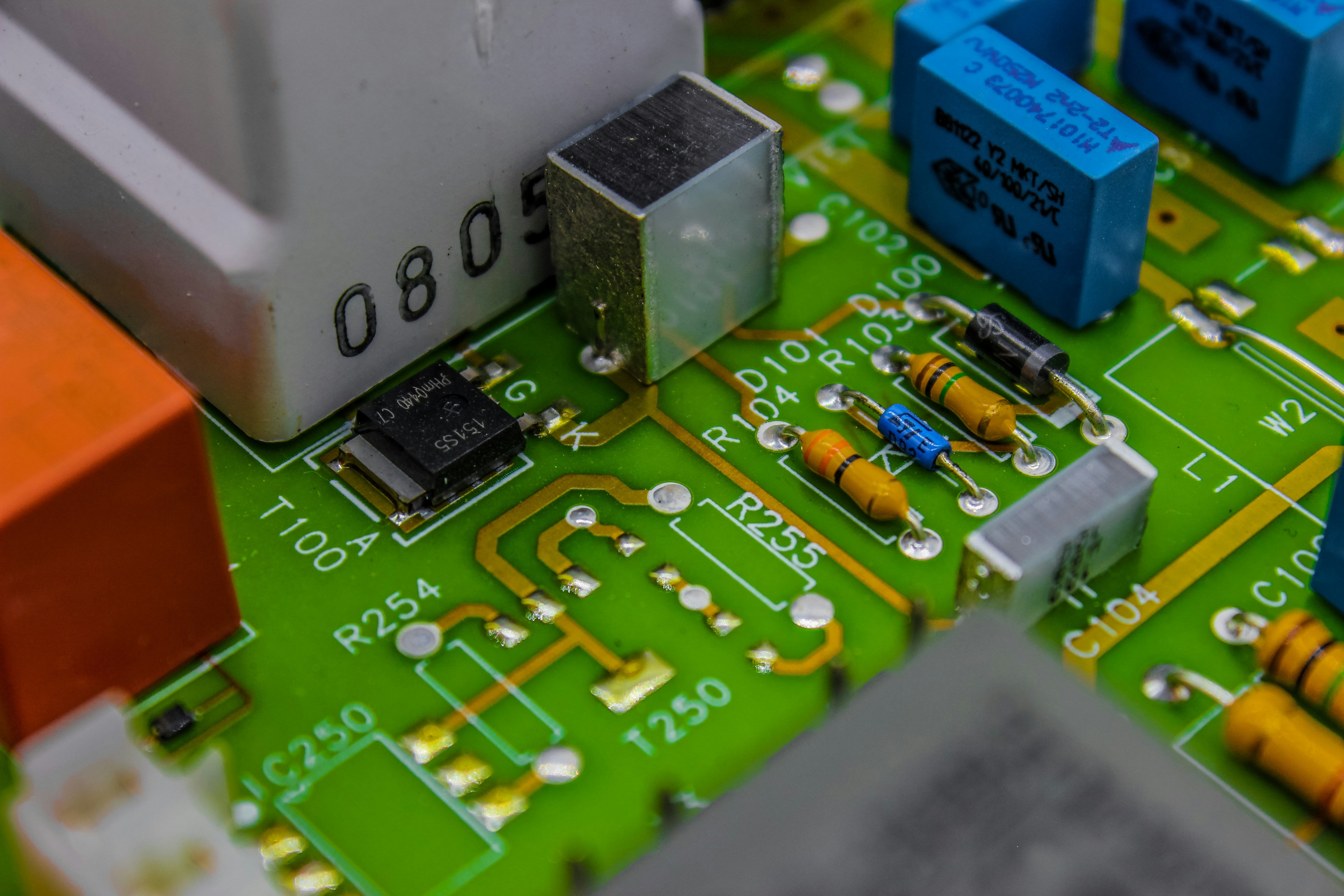
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) refers to a method of electronic circuit assembly where components are mounted directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs). This technology contrasts with traditional methods, allowing for more compact designs and higher component density. The evolution of SMT has transformed how electronics are manufactured, making it essential in today's fast-paced tech world.
Definition of SMT
At its core, Surface Mount Technology is all about efficiency and precision in assembling electronic components. Unlike through-hole technology, where leads are inserted into holes in the PCB, SMT involves affixing components directly to the board's surface. This approach results in a more streamlined manufacturing process and enables the use of smaller components, which is crucial for modern electronics.
Historical Development of SMT
The journey of Surface Mount Technology began in the 1960s when engineers sought ways to create smaller and more efficient electronic devices. Initially adopted by military and aerospace industries due to their stringent requirements for reliability and performance, SMT gained traction in consumer electronics during the 1980s. As advancements continued, SMT machines became more sophisticated, paving the way for widespread adoption across various sectors—answering questions like What is the SMT used for? with diverse applications from smartphones to medical equipment.
Key Characteristics of Surface Mount
Key characteristics that define Surface Mount Technology include its compact size, reduced weight, and ability to support high-speed production processes. Components used in SMT systems typically have no leads or very short leads that facilitate direct mounting on PCBs—making them less prone to damage during assembly compared to traditional methods. Furthermore, these characteristics allow manufacturers to achieve higher packing densities on boards while maintaining excellent electrical performance—a significant advantage over older techniques.
What is the SMT Used For?
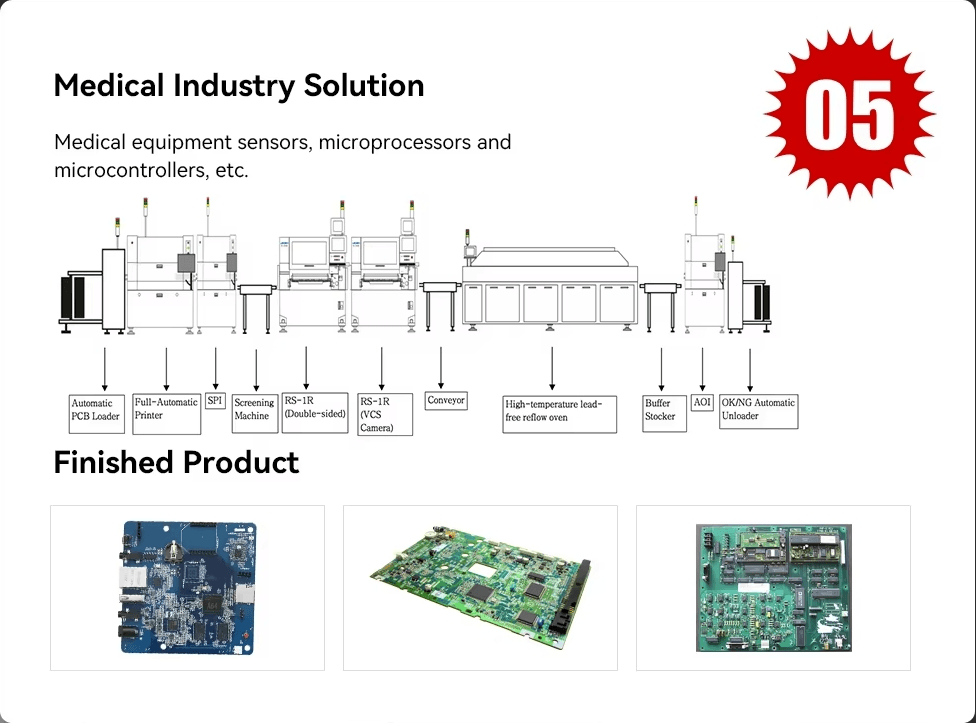
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) has revolutionized the electronics manufacturing landscape, becoming integral to various industries. But what is the SMT used for? The applications of SMT are vast, ranging from consumer electronics to automotive manufacturing and critical medical devices.
Applications in Consumer Electronics
In the realm of consumer electronics, surface mount systems are ubiquitous. From smartphones to laptops, these compact and efficient devices rely heavily on SMT machines for their assembly. The ability to place components directly onto circuit boards without needing holes allows for thinner designs and improved performance—essential factors in today's fast-paced tech market.
Moreover, consumer gadgets benefit from the high density and reliability that SMT technology offers. With smaller components fitting snugly on circuit boards, manufacturers can create sleeker products without compromising functionality. This efficiency translates into lower production costs and faster turnaround times—an absolute win-win for both producers and consumers alike.
Role in Automotive Manufacturing
The automotive industry has also embraced surface mount systems with open arms, as safety and reliability are paramount in vehicle design. What does surface mount mean in this context? It means that essential electronic components—like sensors, control units, and communication modules—are mounted directly onto printed circuit boards (PCBs), enhancing durability while saving space.
Automakers utilize SMT machines to ensure that vehicles are equipped with advanced features such as anti-lock braking systems (ABS) or adaptive cruise control—all made possible through precise electronic integration. As vehicles become increasingly reliant on sophisticated electronics for performance and safety, understanding what is the SMT used for becomes crucial for manufacturers striving to meet regulatory standards while delivering high-quality products.
Importance in Medical Devices
In healthcare technology, the importance of surface mount technology cannot be overstated. Medical devices often require high precision; thus, what is the difference between SMT and SMD becomes a critical consideration when designing equipment like pacemakers or diagnostic imaging machines. Surface mount components facilitate miniaturization without sacrificing functionality—a necessity when you’re working with life-saving devices.
SMT technology helps create compact medical instruments capable of performing complex tasks while ensuring patient safety through reliable operation over extended periods. With innovations continually emerging in this field, it’s evident that embracing a robust surface mount system can lead to groundbreaking advancements in medical care.
In summary, whether it's enhancing our everyday gadgets or ensuring our cars run smoothly and safely—or even saving lives—the applications of Surface Mount Technology are extensive and vital across multiple sectors today.
What Does Surface Mount Mean?
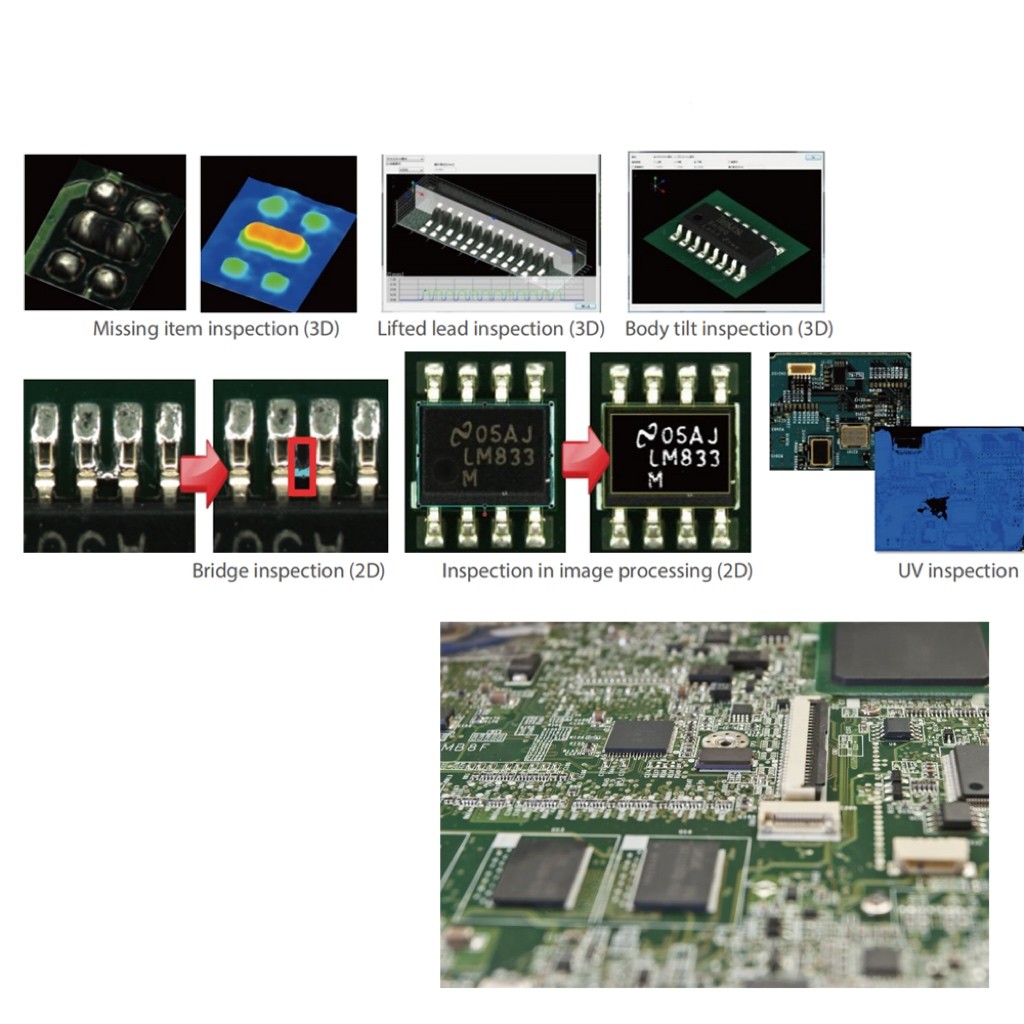
Surface mount technology (SMT) refers to a method of mounting electronic components directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs). This technique has revolutionized how we design and manufacture electronics, allowing for smaller, more efficient devices. Understanding what surface mount means is crucial for anyone involved in electronics manufacturing or design.
Explanation of Surface Mount Components
Surface mount components are specially designed to be soldered onto the PCB without requiring any holes for insertion. These components come in various shapes and sizes, including resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits, all optimized for SMT processes. The beauty of a surface mount system is that it allows for higher component density and improved electrical performance due to shorter connection paths.
Comparison with Through-Hole Technology
When comparing surface mount technology with through-hole technology, several key differences emerge. Through-hole components require drilling holes into the PCB, which can lead to larger designs and increased manufacturing costs. Conversely, SMT machines facilitate a more compact layout by eliminating the need for holes, resulting in lighter and smaller devices that are easier to assemble.
Advantages of Surface Mount Design
The advantages of using a surface mount design are numerous and impactful on modern electronics manufacturing. First off, SMT technology enables faster production rates because components can be placed closer together on the board—this means less time spent assembling devices. Additionally, surface-mounted components typically exhibit better performance characteristics due to their reduced inductance and capacitance compared to their through-hole counterparts.
What is the Difference Between SMT and SMD?
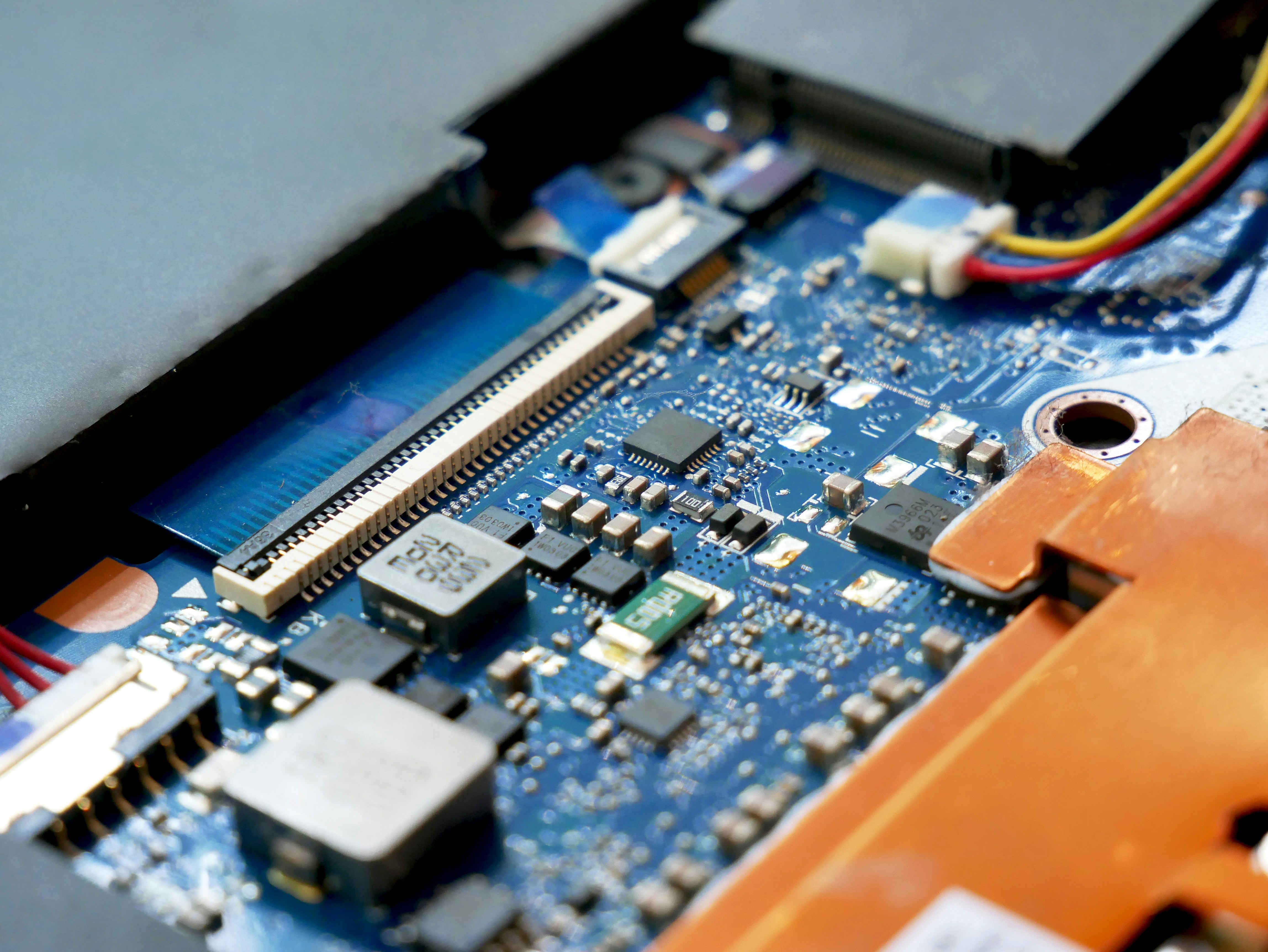

When diving into the realm of electronics, it's essential to distinguish between two commonly used terms: Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Surface Mount Devices (SMD). While they are often used interchangeably in casual conversation, they refer to different aspects of electronic assembly. Understanding this difference can clarify what is involved in a surface mount system and how SMT machines function.
Definition of SMT vs SMD
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) encompasses the entire process of mounting electronic components directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs). This technique revolutionized electronics manufacturing by allowing for more compact designs and higher component density. On the other hand, Surface Mount Devices (SMD) are specific components designed for use with SMT; these devices do not have leads that go through the PCB but instead have pads that sit on top, making them ideal for automated assembly processes.
Component Differences and Similarities
While both SMT and SMD are integral to modern electronics, their roles differ significantly within a surface mount system. SMT refers to the technology used in assembling circuits, while SMD refers specifically to the components that utilize this technology. However, both share common ground in their ultimate goal: creating efficient and reliable electronic devices that can fit into our increasingly compact world.
In terms of similarities, both SMT and SMD contribute to enhanced performance metrics such as reduced size and weight compared to traditional through-hole components. Moreover, they enable faster manufacturing processes thanks to advanced SMT machines designed for high-speed production lines. Ultimately, understanding these differences helps clarify what is the SMT used for across various applications.
Industry Terminology Clarified
In the fast-paced world of electronics manufacturing, clarity in terminology is crucial. Many industry professionals may use SMT when referring to both technology and devices out of convenience; however, distinguishing between them fosters better communication regarding project specifications or technical requirements. Recognizing that What does surface mount mean? relates primarily to technology while What is the difference between SMT and SMD? addresses component specifics can streamline discussions about design choices or production methods.
As we navigate this landscape filled with acronyms like SMT and SMD, it’s vital to appreciate their respective roles within a surface mount system as well as their contributions toward advancing SMT technology overall. By doing so, manufacturers can optimize their processes while ensuring quality output in consumer electronics, automotive parts, medical devices, and more.
Overview of SMT Technology
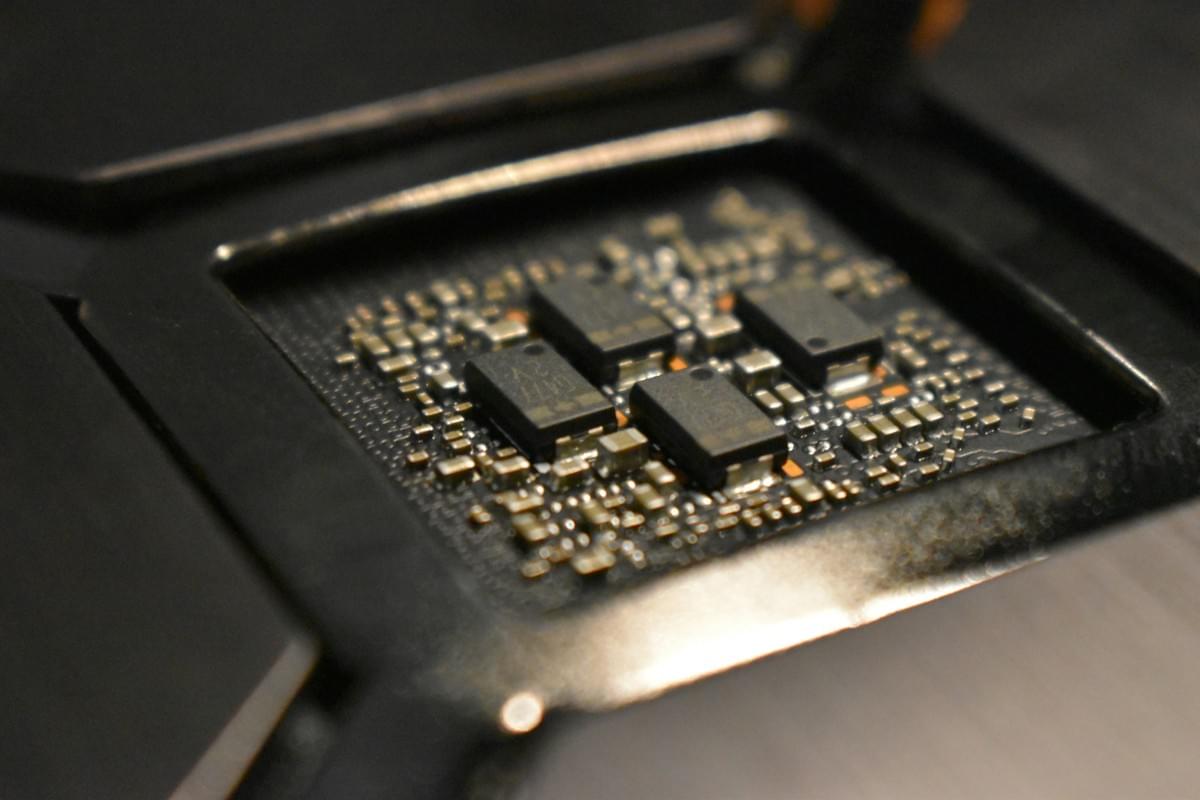
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) has transformed the landscape of electronics manufacturing, becoming a cornerstone of modern production lines. As we delve into the current trends, innovations in SMT machines, and the future of surface mount systems, it is evident that this technology continues to evolve rapidly. Understanding these aspects will illuminate why SMT is so vital in today's electronic devices.
Current Trends in SMT
One of the most notable trends in SMT technology is miniaturization. Manufacturers are increasingly pushing for smaller components that fit into compact designs without sacrificing performance. This trend has led to a surge in demand for advanced surface mount systems capable of handling intricate layouts and dense circuitry.
Moreover, automation plays a crucial role in current SMT practices. With the rise of Industry 4.0, manufacturers are integrating IoT-enabled machines that enhance efficiency and reduce human error during assembly processes. As we explore what is the SMT used for?, it becomes clear that these automated systems are essential for meeting the high demands of various industries.
Another significant trend is sustainability within SMT operations. Companies are focusing on eco-friendly materials and processes to reduce waste and energy consumption during production. This commitment not only benefits the environment but also aligns with consumer preferences for greener products, making understanding what does surface mount mean? all the more relevant as manufacturers adapt to these changes.
Innovations in SMT Machines
The evolution of SMT machines has introduced groundbreaking innovations that enhance productivity and precision. For instance, advancements in pick-and-place technology have allowed machines to place components with incredible accuracy at high speeds. These state-of-the-art machines can handle various component sizes while maintaining quality control—a critical factor when discussing what is the difference between SMT and SMD?
Furthermore, software integration has become a game-changer for operators managing surface mount systems. Real-time monitoring tools provide insights into machine performance and product quality, enabling quick adjustments to minimize downtime or defects during production runs. As we consider how these innovations impact what is the SMT used for?, it's clear they streamline operations across diverse applications.
Lastly, 3D printing technology is beginning to influence how some components are designed and produced within surface mount technology frameworks. By allowing rapid prototyping and customization, manufacturers can respond swiftly to market needs while reducing lead times significantly—an essential capability as competition intensifies globally.
Future of Surface Mount Systems
Looking ahead, the future of surface mount systems appears bright with continued advancements on multiple fronts. One key area will be artificial intelligence (AI) integration into manufacturing processes; AI could optimize production schedules based on real-time data analysis while predicting maintenance needs before issues arise—enhancing overall efficiency significantly.
Additionally, there’s an increasing focus on developing smarter materials that can adapt their properties based on environmental conditions or user requirements; this shift could redefine applications across consumer electronics and beyond when considering what does surface mount mean? The potential benefits include enhanced durability and functionality tailored specifically to user needs.
Finally, as global supply chains evolve post-pandemic disruptions, resilience will be paramount in ensuring consistent access to raw materials necessary for producing advanced SMT components efficiently—making adaptability crucial within this industry landscape moving forward! Embracing these changes will ensure manufacturers remain competitive while leveraging cutting-edge technologies associated with Surface Mount Technology.
Conclusion
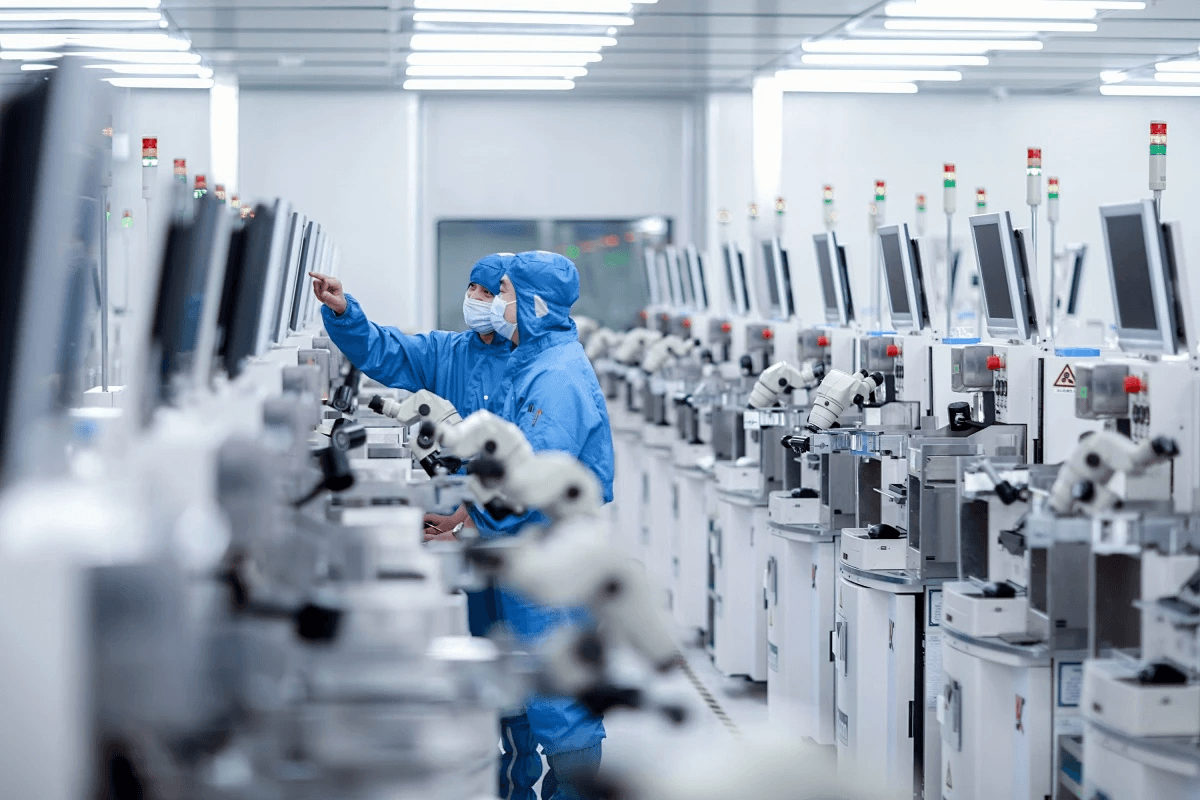

As we wrap up our exploration of Surface Mount Technology (SMT), it's clear that this innovative approach to electronics manufacturing has revolutionized the industry. With its compact design and efficiency, the surface mount system is integral to modern devices, enabling higher performance in smaller packages. Understanding what SMT is used for and its advantages over traditional methods can empower manufacturers to make informed decisions.
Key Takeaways on Surface Mount Technology
Surface Mount Technology has transformed the way electronic components are assembled, allowing for greater density and improved reliability. The key characteristics of SMT include a smaller footprint, reduced assembly time, and enhanced performance—all crucial factors in today's fast-paced market. Moreover, knowing what the difference is between SMT and SMD can clarify misconceptions and highlight their respective roles in electronics design.
The Role of Bensun in SMT Solutions
Bensun stands out as a leader in providing cutting-edge SMT machines that cater to various manufacturing needs. By leveraging advanced SMT technology, Bensun ensures that clients receive efficient solutions tailored to their specific production requirements. With a commitment to innovation and quality, Bensun plays a pivotal role in enhancing the capabilities of surface mount systems across industries.
Why Embrace SMT in Electronics Manufacturing
Embracing Surface Mount Technology is essential for electronics manufacturers aiming to stay competitive in an ever-evolving landscape. The advantages of using a surface mount system—such as increased production speed and lower costs—cannot be overlooked when assessing future strategies. As we continue into an era dominated by smart devices, understanding what surface mount means becomes vital for businesses looking to thrive.
