Introduction
In the ever-evolving world of electronics, understanding surface mount technology is crucial for anyone looking to stay ahead. This innovative method has transformed how components are assembled onto circuit boards, leading to smaller, more efficient devices. But what exactly is surface mount technology? Let's dive into its benefits, applications, and how it has reshaped the electronics landscape.
Understanding Surface Mount Technology
Surface mount technology (SMT) refers to a method of mounting electronic components directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs). Unlike traditional through-hole methods that require holes in the PCB, SMT allows for a more compact design by using smaller components that can be soldered directly to the board's surface. This shift not only enhances performance but also enables manufacturers to produce lighter and more reliable electronic devices.
Benefits of Implementing SMT
Implementing SMT comes with numerous advantages that make it an attractive choice for manufacturers and designers alike. For starters, the SMT process allows for higher component density on PCBs, which means more functionality in less space—a critical factor in today’s miniaturized devices. Additionally, this technology promotes faster production speeds and improved reliability due to reduced mechanical stress on solder joints.
Common Applications of SMT
So, what is SMT used for? The applications are vast and varied; from consumer electronics like smartphones and laptops to industrial machinery and automotive systems, SMT plays a pivotal role across industries. Its ability to support high-speed assembly processes while maintaining quality makes it indispensable in modern manufacturing practices—showcasing why understanding surface mount technology is essential for anyone involved in electronics.
What is Surface Mount Technology?
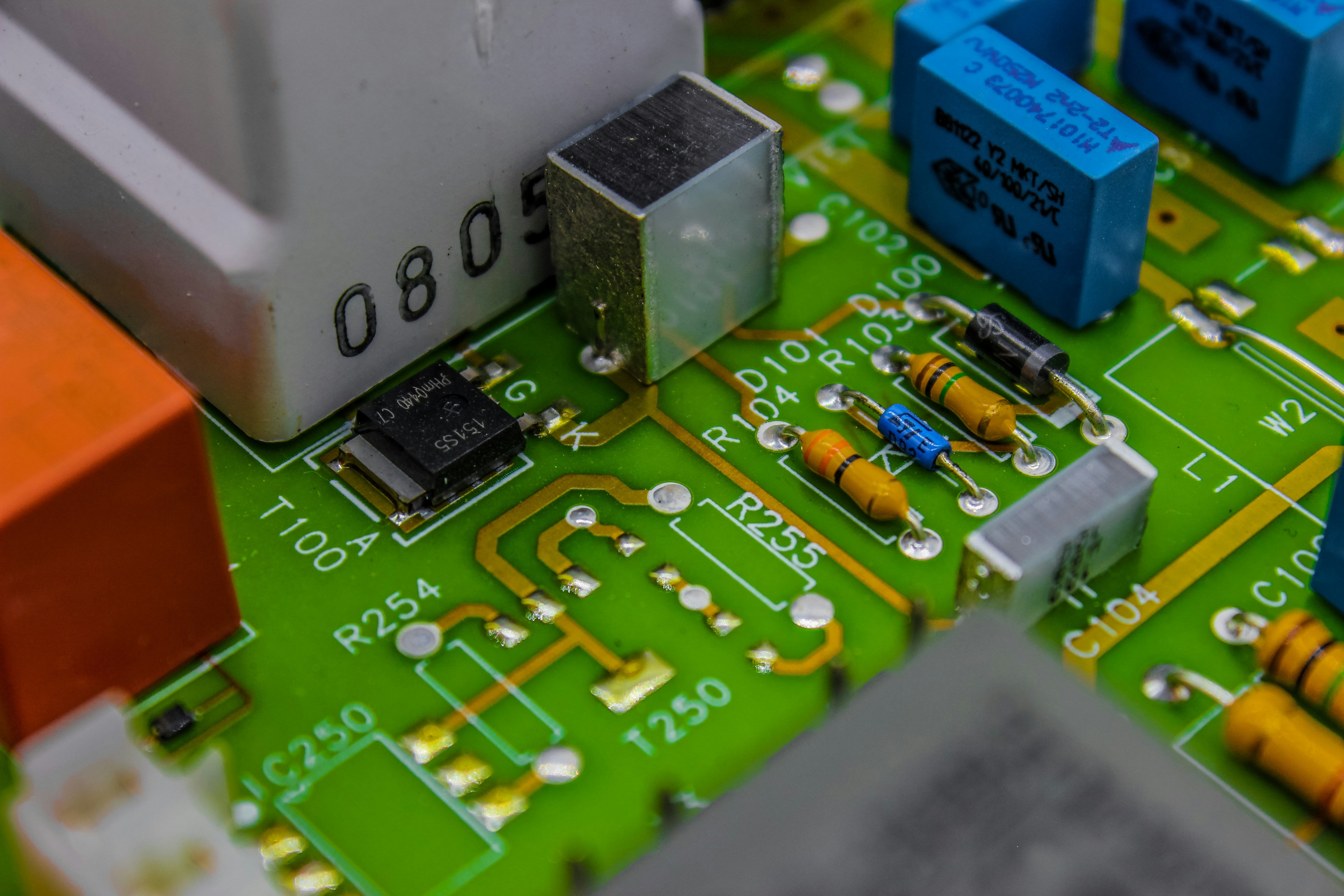
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is a revolutionary method in the electronics manufacturing industry that allows components to be mounted directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs). This innovative approach has transformed how electronic devices are assembled, enabling smaller, lighter, and more efficient products. So, what is surface mount technology? It’s essentially the art of placing tiny electronic components on PCBs without the need for through-hole technology, which can be bulky and cumbersome.
Defining Surface Mount Technology
At its core, surface mount technology refers to a technique where electrical components are soldered directly onto the surface of PCBs. Unlike traditional methods that require holes drilled through the board for component leads, SMT employs flat or short leads that sit flush against the board's surface. This not only simplifies assembly but also opens up new avenues for miniaturization in electronics design.
Key Components in SMT
The key components involved in SMT include resistors, capacitors, diodes, and integrated circuits (ICs), all designed specifically for this mounting style. These components come with small footprints and are engineered to fit snugly on PCB surfaces without sacrificing performance. Additionally, specialized solder paste is used during the SMT process to ensure strong electrical connections while maintaining precision—a critical aspect when discussing how does surface mounting work?
Advantages Over Traditional Methods
One of the most significant advantages of using surface mount technology over traditional methods is its ability to support high-density circuit designs. With smaller component sizes and reduced lead lengths, SMT allows manufacturers to produce compact devices that consume less space—ideal for today’s portable gadgets! Furthermore, SMT typically offers improved performance due to shorter signal paths and better thermal management compared to older methods.
How Does Surface Mounting Work?
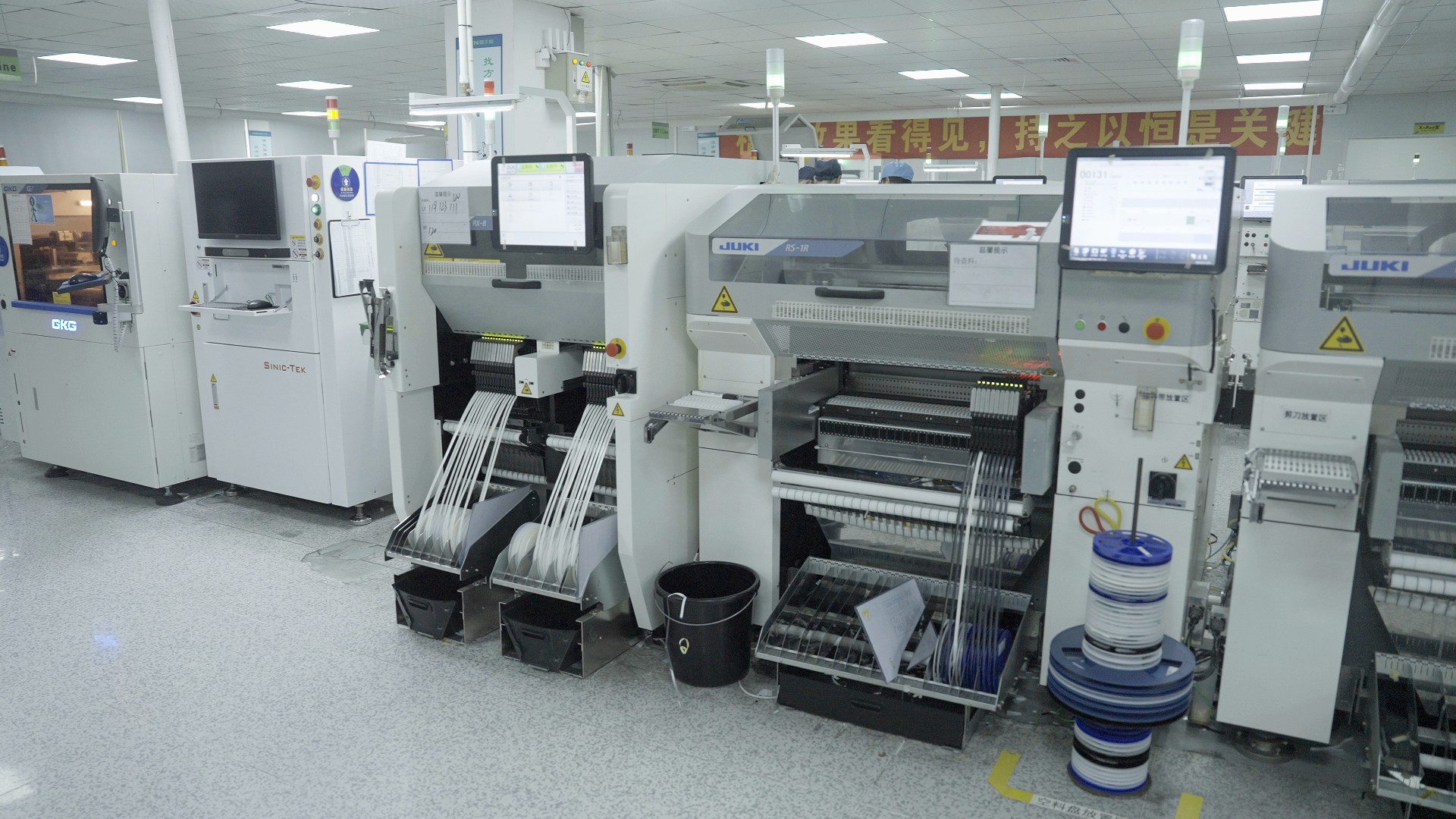

Surface mount technology (SMT) is a cornerstone of modern electronics assembly, but how does it actually work? The process involves attaching electronic components directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs), a technique that has revolutionized the way we design and manufacture electronic devices. Understanding this intricate process gives us insight into the efficiency and effectiveness of SMT in today’s fast-paced tech landscape.
The SMT Process Explained
The SMT process kicks off with the preparation of the PCB, which includes applying a solder paste to specific areas where components will be placed. This paste acts as both an adhesive and a conductor, ensuring that each component stays securely attached during soldering. After placing components on the solder paste, they undergo reflow soldering, where heat melts the paste to create strong electrical connections—voilà, your surface mount technology assembly is complete!
This streamlined approach not only speeds up production but also allows for higher component density on PCBs compared to traditional through-hole methods. With fewer manual steps involved, manufacturers can achieve greater consistency and reduce labor costs significantly. Ultimately, understanding how surface mounting works reveals why it’s so widely adopted in various applications.
Equipment Used in Surface Mounting
To execute the SMT process effectively, several specialized pieces of equipment are essential. At the heart of this operation is the pick-and-place machine, which automates the placement of components onto PCBs with remarkable precision and speed—this is where technology truly shines! Additionally, stencil printers are utilized to apply solder paste accurately to designated areas on PCBs before components are placed.
Reflow ovens play a crucial role too; they ensure that solder joints are formed correctly by heating up the entire assembly uniformly after component placement. Other equipment like inspection machines help verify that every component is correctly positioned and properly soldered—quality control is paramount in surface mount technology! With these tools working harmoniously together, manufacturers can produce high-quality electronics at scale.
Importance of Precision in SMT
Precision is everything when it comes to surface mount technology; even minor misalignments can lead to significant issues down the line. In an industry where miniaturization is key, ensuring that each component fits perfectly on its designated spot isn't just important—it's vital for functionality! The accuracy achieved through advanced machinery means fewer defects and reduced need for rework or repairs later in production.
Moreover, precision impacts performance as well; well-aligned components contribute to better signal integrity and overall device reliability. As we explore what SMT is used for across various industries—from consumer electronics to automotive systems—the importance of precision becomes even more apparent when considering safety-critical applications like medical devices or aerospace technologies. In essence, mastering precision within SMT processes not only enhances product quality but also builds trust with consumers who rely on these technologies daily.
What is the Difference Between SMT and SMD?

When diving into the realm of electronics, one often encounters the terms Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Surface Mount Devices (SMD). While they are commonly used interchangeably, understanding their distinctions is crucial for anyone involved in PCB design or manufacturing. SMT refers to the overall process of mounting components on a circuit board's surface, while SMD specifically denotes the actual components used in this process.
Clarifying SMT vs. SMD
To clarify, Surface Mount Technology encompasses all methods and techniques employed to attach electronic components to a PCB without requiring through-holes. In contrast, Surface Mount Devices are the specific types of components designed for this method, such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits. Understanding this difference helps demystify how surface mount technology operates within electronics manufacturing.
Recognizing that SMT is a broader term allows designers and engineers to focus on both the process and its related components more effectively. This distinction also highlights how advancements in SMT can lead to innovations in SMD design, ultimately improving performance and reliability in electronic devices. When asking what is surface mount technology? it's essential to remember that it’s about both the technique and its specialized components.
Role of SMD in Surface Mount Technology
Surface Mount Devices play a pivotal role within Surface Mount Technology by providing compactness and efficiency that traditional through-hole devices cannot match. These devices are specifically engineered for surface mounting processes, making them integral to modern electronics design. Their smaller size allows for higher component density on PCBs, facilitating more complex circuits within limited space.
Furthermore, SMDs contribute significantly to the speed of production within SMT processes due to their compatibility with automated assembly techniques. This automation reduces labor costs while increasing precision—an essential factor when considering how does surface mounting work? The synergy between SMT methods and SMDs has revolutionized electronic manufacturing by enhancing both performance and scalability.
Impact on PCB Design Choices
The distinction between SMT and SMD significantly influences PCB design choices across various applications. Designers must consider not only component types but also how these choices impact overall board layout, thermal management, and signal integrity when utilizing surface mount technology. The increased density afforded by using SMDs encourages innovative designs but also necessitates meticulous planning during the SMT process.
Moreover, as manufacturers adopt new technologies like advanced soldering techniques or even 3D printing for PCBs, understanding what is SMT used for becomes vital in making informed decisions about materials and processes involved in production. Designers can leverage these insights when deciding which components best suit their projects while optimizing performance based on specific application requirements.
In summary, differentiating between Surface Mount Technology (SMT) as a process and Surface Mount Devices (SMD) as its key components offers valuable insights into modern electronics manufacturing practices. As we continue exploring advancements within this field—such as improved efficiency or enhanced functionality—the importance of understanding these terms remains paramount for anyone engaged with PCB design or production.
What is SMT Used For?
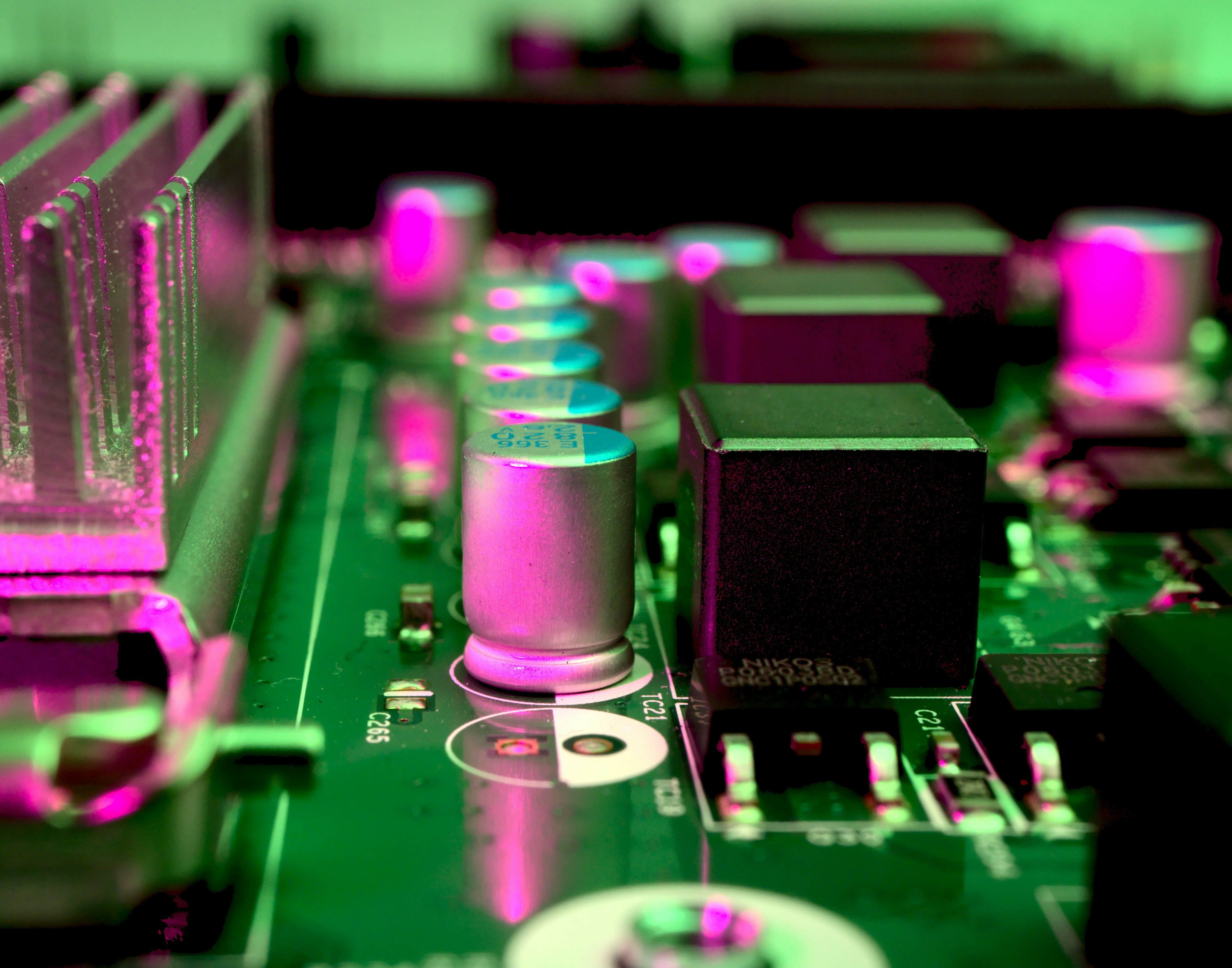
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) has revolutionized the electronics industry, providing a versatile platform for creating compact and efficient devices. Its applications span across various sectors, making it a cornerstone of modern manufacturing. From consumer electronics to automotive systems, SMT plays an integral role in enhancing product functionality and performance.
Applications of SMT in Electronics
What is surface mount technology used for? Well, it’s primarily utilized in the assembly of electronic components onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). This includes everything from smartphones and tablets to medical devices and industrial machinery. The SMT process allows manufacturers to place components such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits with precision, enabling higher component density and improved electrical performance.
Additionally, SMT technology supports diverse applications like LED lighting systems, where compact designs are crucial for efficiency. It also plays a vital role in telecommunications equipment by facilitating high-speed data transmission through miniaturized devices. As we explore how does surface mounting work?, it becomes clear that its adaptability makes it suitable for both high-volume production runs and customized projects.
Industries Benefiting from SMT
The impact of surface mount technology extends across multiple industries that rely on electronics for their operations. The consumer electronics sector is perhaps the most visible beneficiary; products such as laptops, gaming consoles, and smart home devices all utilize SMT to meet consumer demand for smaller and faster gadgets. Automotive manufacturers have also embraced this technology to enhance vehicle systems like navigation controls, sensors, and infotainment units.
Moreover, the medical industry has seen significant advancements due to SMT's capabilities; life-saving devices like pacemakers or diagnostic equipment can now be made smaller while maintaining reliability. Aerospace companies benefit from the lightweight nature of surface-mounted components which contribute to fuel efficiency in aircraft systems. Understanding what is the difference between SMT and SMD helps clarify how these industries leverage unique design advantages offered by this innovative approach.
Case Studies of SMT Implementation
To illustrate the effectiveness of surface mount technology in real-world scenarios, consider a case study involving a leading smartphone manufacturer that adopted advanced SMT processes to enhance device performance while reducing size significantly. By utilizing an optimized surface mount technology process during production, they achieved a 30% reduction in PCB size without compromising functionality or durability.
Another compelling example comes from the automotive sector where a company revamped its engine control unit using SMD components within an SMT framework. This not only improved processing speed but also led to better fuel efficiency ratings due to more precise sensor readings being processed faster than ever before.
These case studies highlight how organizations are reaping benefits from implementing cutting-edge SMT technology into their manufacturing processes—demonstrating its importance across various fields while answering what is SMT used for?
[Image description=assembly line showcasing various electronic components mounted on PCBs using Surface Mount Technology techniques,, workers operating machines,, close-up view of circuit boards., Image name=SMT_Assembly_Line_Image Alt tag=surface mount technology application in modern electronics]
The Surface Mount Technology Process

Surface mount technology (SMT) is a sophisticated method that revolutionizes how electronic components are attached to printed circuit boards (PCBs). Understanding the SMT process is crucial for anyone involved in electronics manufacturing, as it encompasses several detailed steps that ensure precision and reliability. This section delves into the intricacies of the surface mount technology process, highlighting key stages, quality control measures, and innovations that keep SMT at the forefront of modern electronics.
Detailed Steps in SMT Process
The SMT process begins with PCB design, where engineers lay out the board to accommodate various components. Once the design is finalized, manufacturers apply solder paste to specific areas on the PCB using a stencil. Next comes component placement, where automated pick-and-place machines accurately position surface mount devices (SMDs) onto the soldered pads.
After placement, the boards undergo reflow soldering, where they are heated to melt the solder paste and create strong electrical connections between components and PCB pads. Following this step, inspection processes like Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) are employed to catch any defects before moving on to functional testing. These detailed steps in the SMT process ensure that each board meets stringent quality standards while maximizing efficiency.
Quality Control in SMT Production
Quality control is paramount in surface mount technology production; even minor defects can lead to significant failures down the line. Manufacturers implement rigorous testing protocols throughout every stage of production, ensuring that each component adheres to specifications and functions correctly within its intended application. Techniques such as X-ray inspection for hidden solder joints and thermal imaging for detecting overheating components are common practices.
Moreover, continuous monitoring of equipment performance plays a vital role in maintaining high-quality output during mass production runs. By employing statistical process control (SPC), manufacturers can identify trends or anomalies early on and adjust processes accordingly. This commitment to quality not only enhances product reliability but also boosts customer confidence in products utilizing surface mount technology.
Innovations in SMT Technology
The world of surface mount technology is ever-evolving; innovations continually reshape how we approach electronics manufacturing. Recent advancements include improvements in machine vision systems for more accurate component placement and enhanced software solutions for PCB design simulation before physical production begins. These innovations not only streamline operations but also reduce costs associated with errors or rework.
Furthermore, developments such as 3D printing have begun making waves within SMT by enabling rapid prototyping of PCBs with complex geometries that were previously difficult or impossible to achieve using traditional methods. As industries demand smaller devices with increased functionality, these innovations will play a crucial role in meeting those needs while maintaining high standards of performance across various applications of SMT technology.
Conclusion
As we wrap up our exploration of surface mount technology, it's clear that this innovative method has transformed the landscape of electronics manufacturing. From its precise assembly processes to the compact designs it enables, understanding what surface mount technology is and how it works is essential for anyone involved in electronics today. The benefits of SMT are not just theoretical; they have real-world applications that enhance efficiency and performance across various industries.
Key Takeaways on Surface Mount Technology
To summarize, surface mount technology (SMT) allows for smaller, lighter electronic devices by mounting components directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs). The SMT process involves advanced machinery and techniques that ensure high precision, which is crucial for modern electronics. Moreover, distinguishing between SMT and SMD highlights the importance of both in creating effective PCB designs tailored to specific applications.
The Future of SMT in Electronics
Looking ahead, the future of SMT technology appears bright as demand for smaller and more efficient electronic devices continues to grow. Innovations in materials and processes will likely lead to even greater integration capabilities and improved performance metrics in electronic components. As industries evolve with advancements like IoT and AI, surface mount technology will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping next-generation electronics.
Choosing Bensun Technology for SMT Needs
When it comes to selecting a partner for your surface mount technology needs, Bensun Technology stands out as a leader in the field. With expertise in all aspects of the SMT process—from design to production—Bensun ensures quality control at every step while embracing cutting-edge innovations. By choosing Bensun Technology, you’re not just opting for a service; you’re investing in a future where your electronics can thrive thanks to superior surface mount solutions.
