Introduction
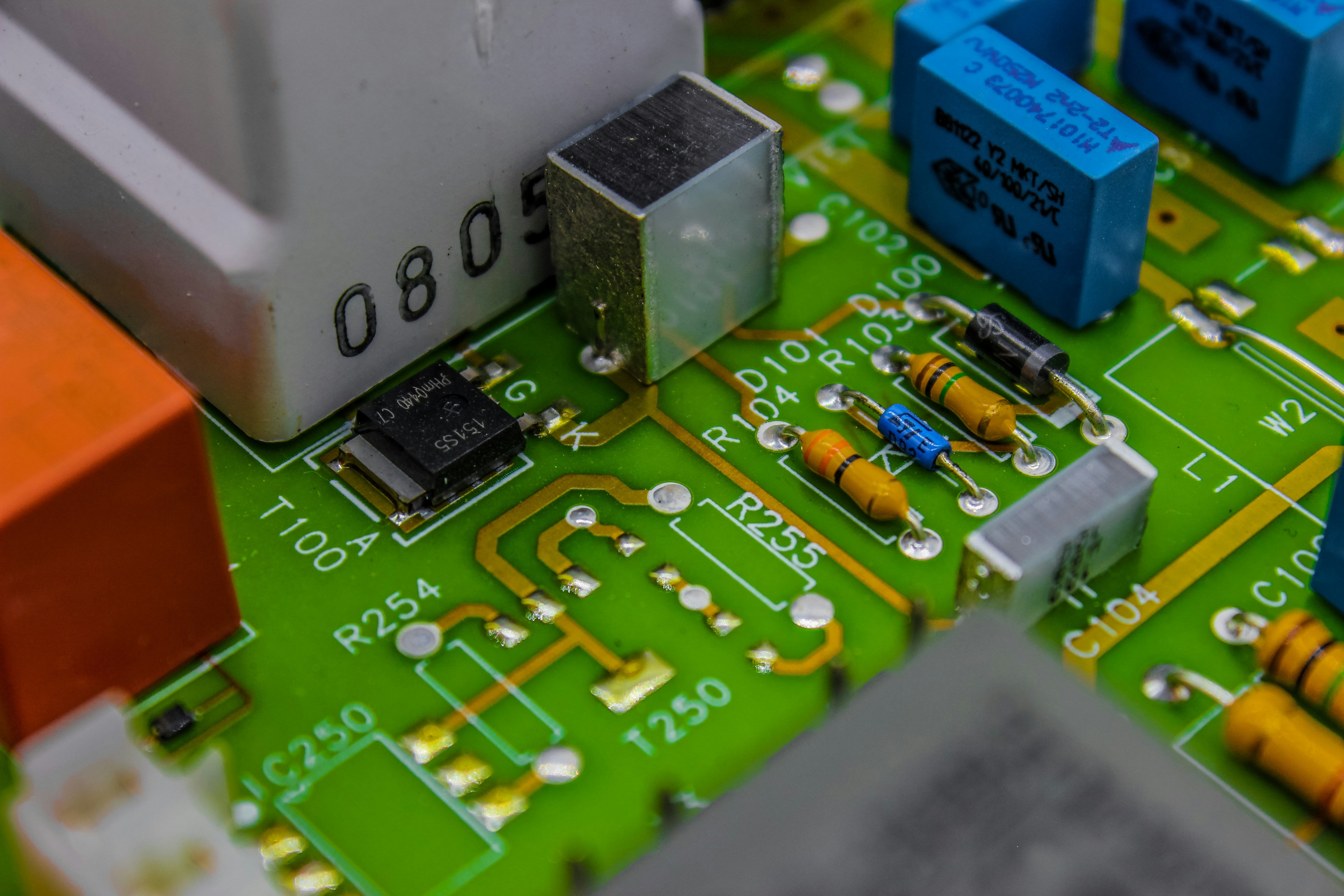
In the fast-paced world of electronics, understanding SMT PCB assembly is crucial for anyone involved in the design and manufacturing of printed circuit boards. So, what is SMT PCB assembly? It refers to the method of mounting components directly onto the surface of a PCB, allowing for more compact designs and higher efficiency. This innovative approach has revolutionized how we build electronic devices, making it essential knowledge for engineers and hobbyists alike.
Understanding SMT PCB Assembly Essentials
To grasp the essentials of SMT PCB assembly, one must first appreciate its foundational components and processes. The term SMT stands for Surface Mount Technology, which contrasts with traditional through-hole techniques where components are inserted into drilled holes on a board. This shift to surface mounting has enabled manufacturers to produce smaller, lighter products with increased functionality.
The Importance of SMT in Modern Electronics
The importance of SMT in modern electronics cannot be overstated; it has become a cornerstone technology that drives innovation across various industries. From smartphones to medical devices, virtually every electronic product benefits from the efficiencies provided by SMT processes. By allowing for greater component density and reducing production costs, SMT has paved the way for more advanced technology that meets consumer demands.
Key Differences: SMD vs. SMT
When navigating the realm of electronics, it's vital to understand key differences between SMD (Surface Mount Device) and SMT (Surface Mount Technology). While SMD refers specifically to the components used in this process, SMT encompasses the entire methodology behind assembling those components onto PCBs. Recognizing these distinctions helps clarify discussions about efficiency and performance when comparing different technologies in PCB design.
What is SMT PCB Assembly?
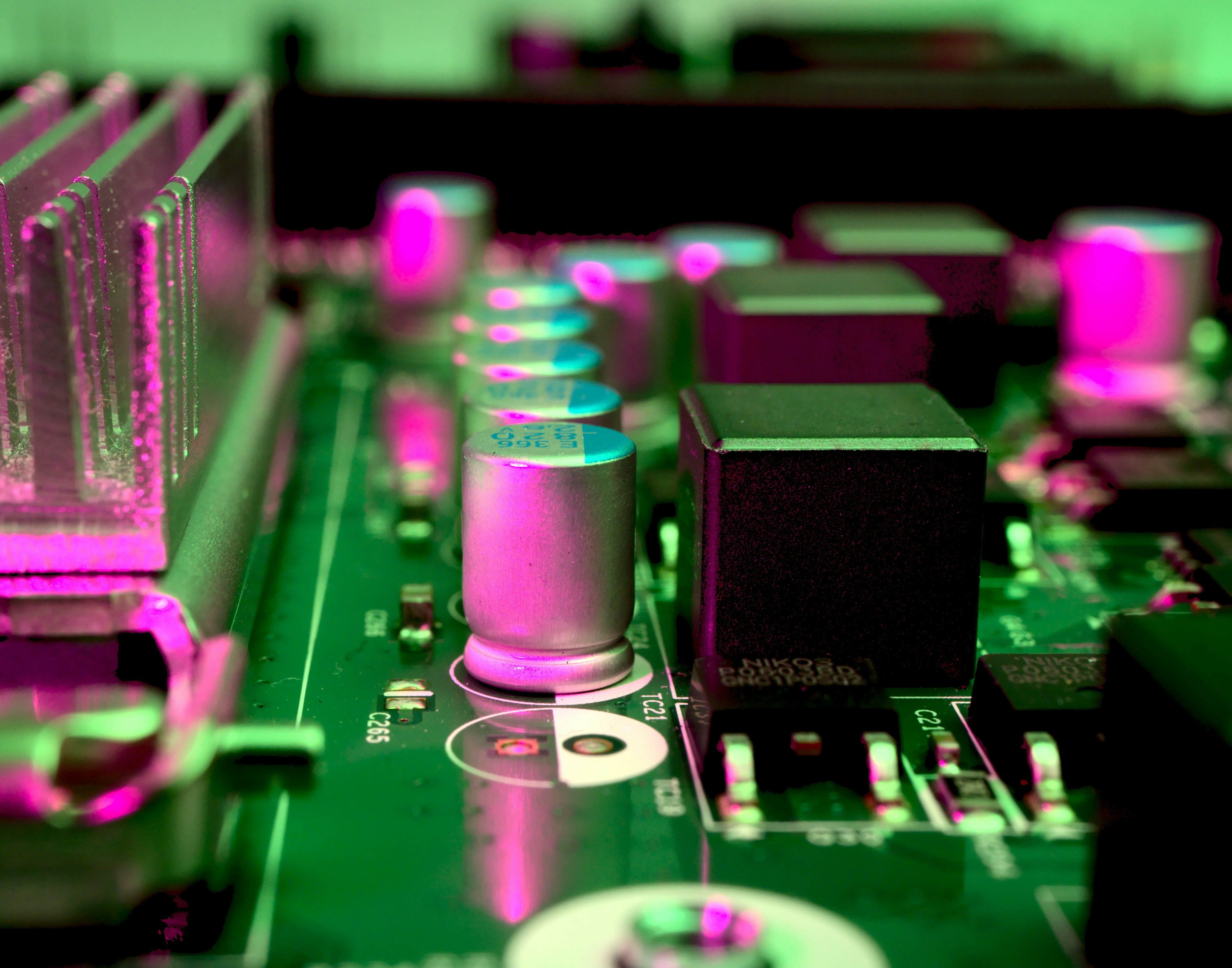
SMT PCB assembly stands at the forefront of modern electronics manufacturing, enabling the production of compact and efficient circuit boards. This technique allows for the mounting of components directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB), as opposed to traditional methods where components are inserted into holes. The result? A sleeker, more reliable product that meets the demands of today’s technology-driven world.
Definition and Overview
So, what is SMT PCB assembly? In essence, it refers to a method of assembling electronic components onto PCBs using Surface Mount Technology (SMT). Unlike through-hole technology, which requires drilling holes in the board for component leads, SMT places components directly on the surface, allowing for higher density and greater performance in electronic devices. This process not only streamlines production but also enhances reliability through improved electrical connections.
Historical Context of SMT Technology
The journey of SMT technology began in the 1960s when engineers sought more efficient ways to design and manufacture electronics. Initially met with skepticism due to its departure from traditional methods, SMT eventually gained traction as its benefits became apparent—most notably in terms of size reduction and assembly speed. Over time, advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques have solidified SMT's place as a cornerstone in PCB assembly processes.
Applications of SMT PCB Assembly
SMT PCB assembly has found its way into an array of applications across diverse industries—from consumer electronics like smartphones and laptops to critical systems such as medical devices and automotive controls. Its ability to support miniaturization while maintaining performance makes it ideal for modern gadgets that boast powerful functionalities within compact designs. Additionally, industries utilizing automation can greatly benefit from the efficiency provided by this assembly process, enhancing productivity while reducing costs.
What is the Difference Between SMD and SMT in PCB?
When diving into the world of electronics, understanding the distinction between SMD (Surface Mount Device) and SMT (Surface Mount Technology) is crucial for anyone involved in SMT PCB assembly. While they are often mistakenly used interchangeably, they refer to different aspects of electronic component assembly. SMD pertains to the actual components that are mounted on a printed circuit board (PCB), while SMT refers to the technology and methods used for mounting these components.
Clarifying SMD and SMT Terminology
To clarify, Surface Mount Devices (SMDs) are electronic components designed specifically for surface mount technology. They come in various shapes and sizes but share one common trait: they do not require through-holes like traditional components, allowing for a more compact design. On the other hand, Surface Mount Technology (SMT) encompasses all processes involved in mounting these devices onto PCBs, including soldering techniques and assembly processes that enhance efficiency.
Understanding this distinction is vital when discussing what is SMT PCB assembly? It's not just about the components; it's also about how they’re assembled onto PCBs using advanced techniques that maximize performance and minimize space. The terminology may seem trivial at first glance, but it plays a significant role in ensuring clarity when designing or manufacturing electronic products.
Performance and Efficiency Comparisons
In terms of performance, SMDs typically offer advantages over traditional through-hole components due to their smaller size and lighter weight. This allows for higher density circuit designs—essentially cramming more functionality into less space without sacrificing performance. When we consider what is the difference between SMD and SMT in PCB? It becomes clear that while SMDs excel at miniaturization, SMT enhances overall efficiency during production.
The efficiency of the SMT process contributes significantly to faster production times compared to conventional methods involving through-hole technology. Automated pick-and-place machines can quickly position thousands of SMDs on a PCB within minutes—something manual soldering could never achieve! This speed translates directly into reduced manufacturing costs, making it an attractive option for companies looking to stay competitive in today's fast-paced electronics market.
Use Cases for Each Technology
When exploring use cases for each technology underlines their practical applications across various industries. For instance, SMDs are prevalent in consumer electronics like smartphones and laptops where space-saving designs are paramount; their compact nature allows manufacturers to create sleek devices with enhanced functionalities. Conversely, traditional through-hole components might still be favored in high-power applications or environments where durability is crucial.
In summary, both technologies have their place within modern electronics design; understanding when to use each can lead to better product outcomes. Whether you're delving into what is the meaning of SMT or looking at specific applications of SMDs versus SM technology within your projects will help streamline your approach during the smt pcb assembly process.
What is the Meaning of SMT?
Surface Mount Technology, commonly referred to as SMT, has become a cornerstone in the realm of electronics and PCB assembly. But what is SMT PCB assembly, and why does it matter? Understanding the meaning of SMT is essential for anyone involved in modern electronic design and manufacturing.
Decoding the Surface Mount Technology
At its core, Surface Mount Technology (SMT) refers to a method where electronic components are mounted directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs). This contrasts with traditional through-hole technology, where components are inserted into holes drilled into the board. The beauty of SMT lies in its ability to allow for more compact designs, enabling manufacturers to create smaller and more efficient devices without compromising performance.
When we talk about what is SMT PCB assembly, we’re referring to this innovative approach that streamlines production processes and enhances device functionality. With reduced space requirements on PCBs, manufacturers can pack more components into a smaller area while also improving electrical performance due to shorter interconnects. This efficiency has made SMT indispensable in today's fast-paced electronics market.
The Evolution of SMT in Electronics
The journey of Surface Mount Technology dates back to the 1960s when it was first introduced as a solution for miniaturizing electronic devices. Initially met with skepticism due to reliability concerns, advancements over time have solidified its place within the industry. By the 1980s, SMT gained traction as manufacturers recognized its potential for reducing costs and increasing production speeds.
As technology advanced further, so did the capabilities of SMT PCB assembly processes. The introduction of automated pick-and-place machines revolutionized how components were assembled onto PCBs, dramatically increasing efficiency and accuracy compared to manual methods. Now considered standard practice across various industries—from consumer electronics to aerospace—SMT continues to evolve alongside innovations like IoT devices and smart technologies.
How SMT Transformed PCB Design
The impact of Surface Mount Technology on PCB design cannot be overstated; it has fundamentally changed how engineers approach circuit layouts and component placement. With SMD (Surface Mount Devices) being smaller than their through-hole counterparts, designers have embraced tighter spacing between components which leads to more intricate designs that were previously unimaginable.
This transformation allows for greater flexibility in design; engineers can now create multi-layered boards packed with functionalities that cater specifically to modern demands—think smartphones or wearable tech! Furthermore, understanding what is the difference between SMD and SMT in PCB helps clarify how these terms relate but also highlights their unique roles within electronic manufacturing.
In summary, understanding what is the abbreviation for SMT in PCB leads us back full circle: it's not just about terminology; it's about recognizing how this technology has reshaped our world by making devices smarter and more efficient than ever before.
What is the Abbreviation for SMT in PCB?

When diving into the world of electronics, you’ll often encounter a plethora of acronyms that can leave even seasoned professionals scratching their heads. One of the most prominent among these is SMT, which stands for Surface Mount Technology. Understanding what SMT PCB assembly entails and how it fits within the broader context of electronics is crucial for anyone involved in this field.
A Brief Look at PCB Acronyms
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are rife with abbreviations that help streamline communication among engineers and manufacturers. Beyond SMT, you might also come across SMD (Surface Mount Device), PCB (Printed Circuit Board), and BOM (Bill of Materials). These acronyms serve as shorthand to convey complex concepts quickly, making discussions about processes like SMT assembly more efficient.
Why Abbreviations Matter in Electronics
Abbreviations are not just a quirk of the industry; they play an essential role in simplifying communication and enhancing understanding among professionals. In an ever-evolving field like electronics, where new technologies emerge frequently, staying updated on terminology can make or break a project. Recognizing what SMT means in conjunction with other terms helps teams collaborate effectively and ensures everyone is on the same page during discussions about SMT processes.
SMT's Role in Industry Jargon
Within industry jargon, SMT has become synonymous with modern efficiency and innovation in PCB design and assembly. It signifies a shift from traditional through-hole technology to more compact surface mount solutions that optimize space while enhancing performance—key aspects that every engineer should appreciate when considering what is the difference between SMD and SMT in PCB? As companies continue to adopt these technologies, understanding their significance becomes increasingly important for navigating conversations around advancements like smt pcb assembly.
The SMT Assembly Process
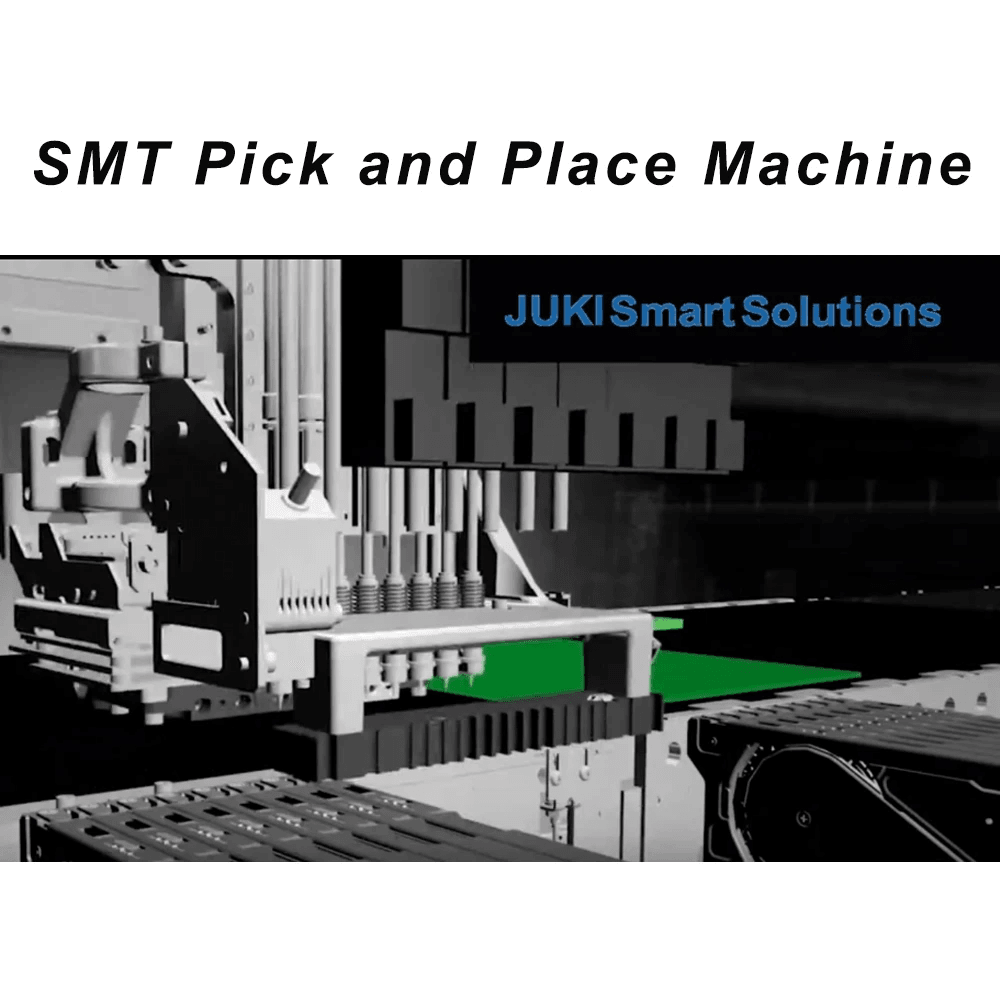
The SMT assembly process is a crucial aspect of modern electronics manufacturing, enabling the efficient and precise placement of components on printed circuit boards (PCBs). Understanding this process helps demystify what is SMT PCB assembly, shedding light on its significance in the industry. By breaking down the steps involved and identifying key players, we can appreciate how this technology has transformed electronic device production.
Step-by-Step Breakdown of SMT Process
The SMT process begins with designing a PCB layout that accommodates surface mount devices (SMDs). This design is then translated into a production file that guides the assembly machines during manufacturing. Next, solder paste is applied to specific areas of the PCB using a stencil, ensuring that only designated pads receive solder for component attachment.
Once the solder paste is in place, SMDs are picked and placed onto the PCB by automated pick-and-place machines. These machines are highly sophisticated and can place thousands of components per hour with remarkable precision. After placement, the board undergoes reflow soldering—where heat melts the solder paste to create strong electrical connections between components and pads—making it a pivotal step in understanding what is SMT PCB assembly.
Finally, post-assembly inspection occurs through techniques like Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) or X-ray inspection to ensure quality control. These inspections verify that all components are correctly placed and properly soldered before moving on to functional testing. This meticulous attention to detail throughout the SMT process highlights its importance in producing reliable electronic devices.
Equipment Involved in SMT Assembly
The equipment used in SMT assembly plays a vital role in ensuring efficiency and accuracy throughout the process. Essential tools include stencil printers for applying solder paste accurately onto PCBs, which set up each board for component placement effectively. Automated pick-and-place machines follow suit, utilizing advanced robotics to position SMDs with pinpoint accuracy.
Reflow ovens are another critical piece of equipment within the SMT assembly process; they create controlled heating environments where solder paste melts and solidifies around component leads during reflow soldering. Additionally, inspection systems such as AOI machines provide essential feedback on potential defects or misalignments after assembly completion. Understanding this array of equipment clarifies what is meant by an effective smt pcb assembly line.
Moreover, other supporting tools like conveyors transport PCBs between stations while managing workflow seamlessly throughout production stages. Each piece of equipment contributes significantly to streamlining operations while maintaining high-quality standards—a hallmark feature when discussing what is the difference between SMD and SMT in PCB manufacturing.
Key Players in the SMT Supply Chain
The success of any smt pcb assembly operation hinges on collaboration among various key players within its supply chain ecosystem. First up are design engineers who conceptualize innovative products requiring careful consideration regarding component selection—this knowledge directly impacts how efficiently SMDs fit into their respective layouts during assembly processes.
Next come manufacturers specializing specifically in producing high-quality SMDs tailored for diverse applications across industries ranging from consumer electronics to automotive sectors; these suppliers must meet stringent quality standards consistently while adapting quickly based on market demands! Lastly but certainly not leastly: contract manufacturers handle large-scale productions by integrating all aspects—from procurement through final testing—to ensure timely delivery without sacrificing quality or performance metrics along each phase: truly embodying teamwork at its finest!
In conclusion, recognizing these roles reveals how interconnected every aspect really becomes when delving deeper into understanding what is meant by “the smt assembly process.” Each participant plays an integral part contributing towards creating reliable electronic devices efficiently—all working together harmoniously within today’s fast-paced technological landscape!
Conclusion

In wrapping up our exploration of SMT PCB assembly, it's clear that this technology is not just a trend but a cornerstone of modern electronics. As we look ahead, the future of SMT PCB assembly appears bright, with continuous advancements promising to enhance efficiency and performance in various applications. Whether you're a seasoned engineer or just starting out, understanding the nuances of what is SMT PCB assembly? is essential for navigating this dynamic landscape.
The Future of SMT PCB Assembly
The future of SMT PCB assembly is poised for exciting developments as manufacturers strive for even smaller and more complex designs. With innovations in materials and techniques, we can expect enhanced reliability and performance from electronic components. Moreover, as industries like IoT and automotive electronics expand, the demand for efficient SMT processes will only increase.
Benefits of Choosing SMT Technology
Choosing SMT technology offers numerous advantages over traditional methods, making it a popular choice among manufacturers. Firstly, the compact nature of surface mount devices (SMD) allows for higher component density on PCBs, effectively saving space without sacrificing functionality. Secondly, the speed and automation involved in the SMT assembly process contribute to faster production times and reduced costs—benefits that are hard to ignore in today’s competitive market.
How Bensun Technology Enhances SMT Solutions
Bensun Technology stands out by providing innovative solutions that enhance the entire SMT process from design to production. Their expertise ensures that clients receive high-quality assemblies tailored to their specific needs while optimizing efficiency throughout the supply chain. By leveraging advanced technologies and industry best practices, Bensun significantly contributes to elevating standards in smt pcb assembly across various sectors.
