Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, understanding the surface mounted device (SMD) is crucial for grasping how modern electronics are designed and manufactured. Surface mounted devices have revolutionized the way we create circuits, allowing for greater efficiency and compactness than traditional methods. This introduction will explore the significance of SMDs and their pivotal role in modern manufacturing practices.
Understanding the Surface Mounted Device
What are surface-mounted devices? At their core, these components are designed to be mounted directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs), eliminating the need for through-hole connections. This innovative approach not only saves space but also enhances performance by reducing signal path lengths, making SMDs a popular choice in various electronic applications.
The Evolution of Electronics with SMD
The evolution of electronics with SMD has been nothing short of revolutionary. As technology progressed, manufacturers began to recognize that traditional methods were limiting their design capabilities and production efficiency. The shift towards surface-mounted devices marked a turning point, enabling more complex circuits to be developed while maintaining smaller form factors.
Importance of SMT in Modern Manufacturing
What is SMT used for? Surface Mount Technology (SMT) plays a critical role in modern manufacturing by streamlining assembly processes and improving reliability across various industries. From consumer electronics to automotive applications, SMT's ability to accommodate high-density designs has made it indispensable in ensuring that products meet today's demanding specifications while optimizing production costs.
What are Surface-Mounted Devices?

Surface-mounted devices (SMDs) have revolutionized the world of electronics, bringing a new level of efficiency and compactness to circuit design. But what exactly are surface-mounted devices? In essence, SMDs are electronic components that are mounted directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs), as opposed to being inserted through holes, which was the traditional method. This mounting technique allows for a more streamlined construction and has become a staple in modern electronics.
Definition and Key Features
A surface-mounted device is characterized by its small size and flat configuration, making it ideal for high-density applications. Unlike their through-hole counterparts, SMDs require specific soldering techniques such as reflow or wave soldering for attachment to PCBs. Key features include their lightweight design, reduced footprint, and compatibility with automated assembly processes, all of which contribute to their widespread adoption in various industries.
Common Applications in Tech
So, where do we find these nifty little components? Surface-mounted devices are ubiquitous in consumer electronics—think smartphones, tablets, and laptops—all relying on SMD technology for compactness and efficiency. They're also prevalent in automotive systems for functions like engine control units (ECUs) and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), as well as in medical devices where space is often at a premium.
Advantages Over Traditional Methods
The advantages of using surface-mounted devices over traditional methods cannot be overstated. First off, SMDs allow for smaller circuit designs due to their compact nature; this means manufacturers can fit more functionality into less space—a win-win! Additionally, the automated assembly processes associated with SMT (Surface Mount Technology) reduce labor costs and increase production speed significantly compared to older methods that require manual insertion.
What is the Difference Between SMD and SMT?
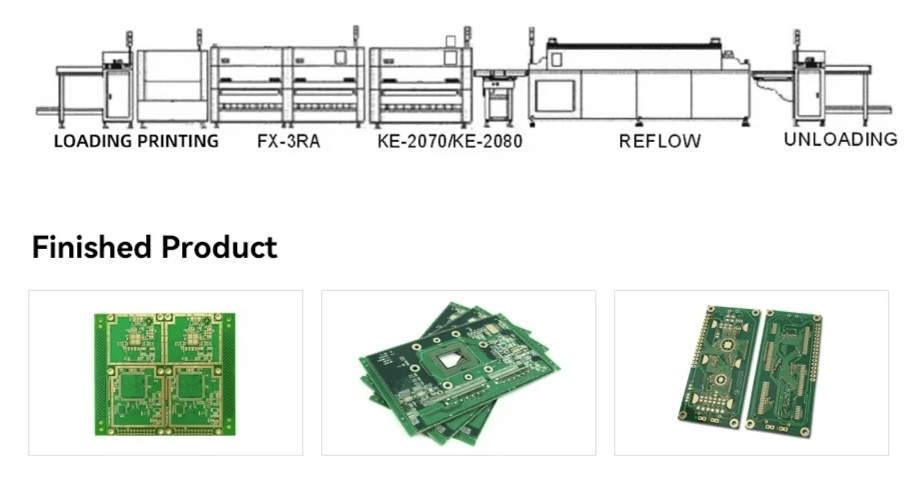
When diving into the world of electronics, you might encounter the terms SMD and SMT frequently. While they are often used interchangeably, it's essential to understand that they refer to different aspects of surface-mounted technology. SMD stands for Surface Mounted Device, which is the actual component, while SMT refers to Surface Mount Technology, the process used to attach these components to circuit boards.
Clarifying the Terms
To clarify, a surface mounted device (SMD) is any electronic component designed for mounting directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). This contrasts with traditional components that require holes drilled into the PCB for insertion. On the other hand, surface mount technology (SMT) encompasses all methods and techniques used in assembling these devices onto PCBs efficiently and effectively.
Understanding what are surface-mounted devices plays a crucial role in distinguishing between SMDs and SMT. While SMDs are about the components themselves—like resistors or capacitors—SMT involves everything from soldering techniques to assembly processes that enable these devices' use in modern electronics. Hence, knowing this difference can help manufacturers optimize their production processes.
Performance Comparisons
When comparing performance between SMD and traditional through-hole components, several factors come into play. Surface mounted devices generally allow for higher circuit density due to their compact size; this means more functionality can fit in a smaller space without sacrificing performance. Additionally, because SMT techniques involve automated assembly processes, they typically yield higher precision and reliability than manual methods used with through-hole designs.
Moreover, one cannot overlook how what does surface-mounted mean impacts performance metrics like thermal management and signal integrity. With better heat dissipation capabilities and reduced inductance paths due to shorter connections on PCBs using SMDs, manufacturers can achieve superior electrical performance compared to older technologies. Thus, understanding these differences is key for engineers looking to enhance product quality.
Cost Implications for Manufacturers
Cost implications are another critical aspect when considering what is SMT used for versus traditional methods involving through-hole technology. Although initial setup costs for SMT may be higher due to specialized equipment needed for placing surface mounted devices accurately on PCBs, long-term savings often outweigh those costs significantly. Automated processes lead to faster production times and lower labor costs over time as well as reduced material waste during assembly.
Additionally, manufacturers often find that adopting SMDs results in lower shipping costs due to their lightweight nature compared with bulkier through-hole components. This translates into more competitive pricing strategies in an increasingly cost-sensitive market environment where every penny counts towards profitability margins. Therefore, understanding what is the difference between SMD and SMT can provide valuable insights into making informed decisions about manufacturing practices.
What Does Surface-Mounted Mean?

Surface-mounted technology (SMT) refers to a method of electronic circuit assembly where components, known as surface mounted devices (SMD), are mounted directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs). This technique contrasts with traditional through-hole technology, where components are inserted into drilled holes. By eliminating the need for holes, SMT allows for more compact designs and greater efficiency in manufacturing.
Explaining the Technology
To grasp what surface-mounted means, one must first understand how SMDs function. These devices have leads that are soldered directly onto the PCB’s surface rather than through it. This not only reduces the space required for each component but also simplifies the assembly process, making it a preferred choice in modern electronics.
The beauty of SMT lies in its ability to accommodate a variety of component sizes and types, allowing manufacturers to create complex circuits with minimal real estate. With advancements in technology, SMDs can now be found in everything from smartphones to household appliances. The flexibility and versatility offered by this approach have revolutionized how we think about electronic design.
Impact on Circuit Design
Understanding what does surface-mounted mean is crucial for appreciating its impact on circuit design. With SMDs taking center stage, designers can create more intricate layouts without worrying about the limitations imposed by through-hole components. This freedom leads to higher density designs that can incorporate more functionality within a smaller footprint.
Moreover, because SMDs can be placed on both sides of a PCB, this dual-surface utilization maximizes available space and enhances overall performance. Designers also benefit from reduced parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can improve signal integrity—an essential factor in high-speed applications. Thus, knowing what are surface-mounted devices helps engineers make informed decisions during the design phase.
How It Enhances Efficiency
The efficiency gains from using SMT over traditional methods cannot be overstated when discussing what is SMT used for in various industries. The automated assembly processes associated with SMDs significantly reduce production time and labor costs while increasing output quality and consistency. As a result, manufacturers can scale their operations without compromising on quality or performance.
Additionally, because surface mounted devices allow for tighter packing of components on PCBs, they contribute to lighter and smaller product designs—an essential aspect in today’s tech-driven world where portability is king. In sectors such as consumer electronics and automotive industries specifically, these efficiencies translate into faster time-to-market and enhanced competitiveness among brands vying for consumer attention.
In summary, understanding what does surface-mounted mean reveals its profound implications across multiple facets of electronics manufacturing—from design flexibility to operational efficiency—all thanks to the innovative use of SMD technology.
What is SMT Used For?
Surface Mounted Technology (SMT) has become a cornerstone of modern electronics, significantly influencing various industries. Understanding what SMT is used for can shed light on its versatility and importance in today's technological landscape. From consumer electronics to automotive applications and medical devices, the impact of surface mounted devices (SMD) is profound.
Role in Consumer Electronics
In the realm of consumer electronics, surface mounted devices play a pivotal role in creating compact and efficient products. Devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops rely heavily on SMT for their intricate circuit designs. The use of SMD allows manufacturers to produce smaller, lighter gadgets without sacrificing performance or reliability.
The benefits extend beyond mere size; surface mounted technology enhances production speed and reduces assembly costs. With the ability to place components directly onto the substrate's surface, manufacturers can streamline their processes significantly. This efficiency not only meets consumer demand for sleek designs but also contributes to lower retail prices—a win-win situation!
Applications in Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, what are surface-mounted devices used for? The answer lies in their ability to improve vehicle safety, performance, and connectivity features. From advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) to infotainment units, SMDs are integral to modern vehicles' functionality.
Automakers increasingly adopt SMT because it enables more sophisticated electronic systems within tighter spaces—ideal for today's vehicles packed with technology. Additionally, using surface mounted technology enhances durability against vibrations and temperature changes common in automotive environments. As cars evolve into smart machines with interconnected systems, the need for reliable SMDs becomes even more critical.
Usage in Medical Devices
When it comes to medical devices, understanding what SMT is used for reveals its crucial role in patient care and diagnostics. Surface mounted devices are found in everything from portable diagnostic tools to complex imaging systems like MRI machines. Their compact nature allows healthcare professionals to utilize advanced technology without compromising portability or usability.
Furthermore, SMDs contribute significantly to the reliability of medical equipment—an essential factor when lives are at stake! With stringent regulations governing medical device manufacturing, using high-quality SMT ensures that these products meet safety standards while delivering consistent performance over time. As healthcare continues to innovate with technology integration, the reliance on surface mounted technology will only grow stronger.
Bensun Technology and Surface Mounted Devices

Bensun Technology stands at the forefront of innovation in the realm of surface mounted devices (SMD). With a comprehensive portfolio that includes advanced SMT equipment, Bensun caters to a diverse range of industries, ensuring they meet the ever-evolving demands of modern electronics. From high-speed pick-and-place machines to precision soldering tools, their offerings are designed to enhance efficiency and reliability in manufacturing processes.
Overview of Bensun’s Offerings
At Bensun, what are surface-mounted devices? They are not just components; they represent a paradigm shift in how electronics are assembled. The company provides an extensive lineup of machinery tailored for both small-scale operations and large-scale production lines, ensuring that manufacturers can maximize their output without compromising on quality. Their commitment to integrating cutting-edge technology into their products allows clients to stay competitive in an increasingly demanding market.
Importance of Quality Equipment in SMD
When it comes to surface mounted devices, the quality of equipment used is paramount for achieving superior performance and reliability. Manufacturers who understand what is the difference between SMD and SMT recognize that investing in high-quality machinery directly impacts product yield and operational efficiency. Poor-quality equipment can lead to defects, increased costs, and ultimately compromise customer satisfaction—something no business can afford in today’s fast-paced environment.
How Bensun Innovates in the SMT Space
Bensun continuously pushes boundaries by incorporating innovative features into their SMT solutions that redefine what does surface-mounted mean for manufacturers globally. By leveraging advancements such as AI-driven automation and real-time monitoring systems, they significantly enhance productivity while reducing waste during production cycles. Their focus on research and development ensures that their clients benefit from state-of-the-art technologies designed specifically for various applications—from consumer electronics to automotive parts—demonstrating how versatile SMT can be across different sectors.
Conclusion
In wrapping up our exploration of surface mounted devices (SMD), it’s clear that these components have revolutionized the electronics landscape. From their humble beginnings to their current status as a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, SMDs have changed how we think about technology and efficiency. The future looks bright for surface-mounted devices, with continuous innovations poised to further enhance their capabilities.
The Future of Surface Mounted Devices
The future of surface mounted devices is not just about miniaturization but also about increased functionality and integration. As industries push for smarter, more efficient solutions, SMD technology will likely evolve to meet these demands, paving the way for advanced applications in artificial intelligence and IoT. With this evolution, we can expect even more compact designs without sacrificing performance or reliability.
Why Invest in SMD Technology
Investing in SMD technology is akin to betting on the future of electronics itself; it’s where innovation thrives and efficiency reigns supreme. By utilizing what are surface-mounted devices, manufacturers can achieve higher production speeds and reduced costs while maintaining quality standards. Moreover, embracing SMD technology allows companies to stay competitive in a fast-paced market that increasingly values compactness and performance.
Unlocking Potential with SMT Solutions
Unlocking potential with SMT solutions involves understanding what SMT is used for across various industries—from consumer electronics to medical devices and automotive applications. The shift towards using surface-mounted components has led to significant improvements in circuit design and overall product reliability. By leveraging the advantages offered by SMT, businesses can not only enhance their product offerings but also ensure they are at the forefront of technological advancements.
