Introduction

In the ever-evolving world of electronics, understanding the nuances of Surface-Mount Technology (SMT) is essential for anyone looking to excel in PCB soldering. SMT solder has revolutionized the way components are attached to circuit boards, providing a compact and efficient alternative to traditional methods. With the right tools and materials at your disposal, mastering SMT soldering can lead to impressive results in your electronic projects.
Understanding Surface-Mount Technology
Surface-Mount Technology (SMT) refers to a method where electronic components are mounted directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs). This technique allows for a significant reduction in space, enabling manufacturers to create smaller and more complex devices. By grasping how SMT works and its benefits, you will be better equipped to utilize SMT solder effectively in your projects.
Why Choose SMT Soldering
Choosing SMT soldering comes with a host of advantages that make it appealing for both hobbyists and professionals alike. The precision offered by SMT techniques means you can achieve cleaner connections with less risk of bridging or cold joints, which can plague traditional soldering methods. Additionally, using solder flux and solder paste enhances the quality of your joints while streamlining the entire process—making it easier than ever to create reliable electronics.
Key Tools and Materials Needed
To embark on your journey into the world of SMT soldering, you'll need a selection of key tools and materials that will set you up for success. Essential soldering tools include fine-tipped soldering irons, tweezers for precise component placement, and various types of solder designed specifically for electronics applications. Don't forget about crucial supplies like solder flux and solder paste; these materials play an integral role in ensuring strong connections while preventing oxidation during the PCB soldering process.
What is SMT Solder?
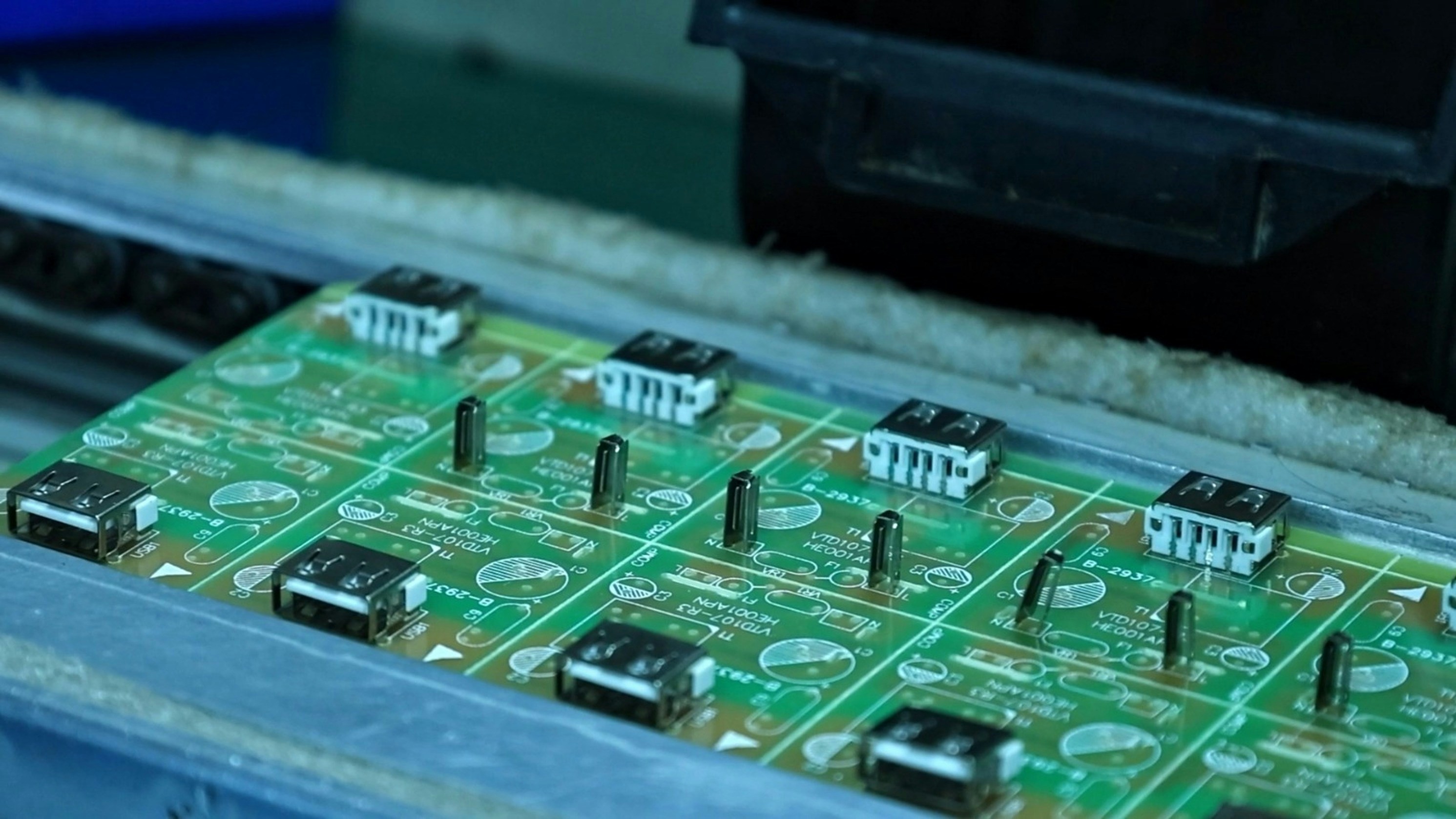
SMT solder is a specialized type of solder used in surface-mount technology (SMT) for assembling electronic components onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). Unlike traditional soldering methods, which often involve through-hole components, SMT solder allows for a more compact design and higher component density. This modern approach to PCB soldering has revolutionized the electronics industry by enabling smaller, lighter devices with improved performance.
Definition and Basic Principles
At its core, SMT solder refers to the materials used to create electrical connections between surface-mounted components and the PCB. Typically, this involves solder paste, which is a mixture of tiny metal particles and flux that facilitates the melting process during heating. The basic principle behind SMT soldering is to apply heat using specialized soldering tools to melt this paste, allowing it to flow into place and solidify upon cooling.
Importance in Modern Electronics
The importance of SMT solder in modern electronics cannot be overstated. As devices become increasingly miniaturized, manufacturers rely on SMT for efficient use of space while maintaining high performance levels. Moreover, the use of advanced smt surface mount technology has led to improved reliability and durability in electronic products due to better thermal management and reduced mechanical stress on components.
Comparison with Traditional Soldering
When comparing SMT soldering with traditional methods, several key differences emerge that highlight the advantages of using SMT techniques. Traditional through-hole soldering requires larger holes drilled into PCBs, making it less suitable for compact designs found in today's gadgets. In contrast, smt surface mount technology allows for greater flexibility in layout design while also reducing production time thanks to automated processes involving precise application of solder paste and flux.
Essential Soldering Tools

When diving into the world of SMT solder, having the right tools can make all the difference between a successful project and a frustrating experience. The essential soldering tools for electronics enthusiasts include everything from soldering irons to specialized equipment designed for precision work. Investing in high-quality tools not only enhances your efficiency but also improves the reliability of your PCB soldering.
Overview of Soldering Equipment
The backbone of any SMT surface mount technology setup is a reliable soldering iron or station, which allows you to apply heat precisely where needed. Additionally, a good pair of tweezers is crucial for handling small components without damaging them, while a magnifying lamp can help you see what you're doing up close—because let's be honest, those tiny components can be sneaky! Don't forget about desoldering pumps and wick; they are invaluable for correcting mistakes when your solder for electronics goes awry.
Recommended Soldering Tips for Precision
Choosing the right soldering tips is essential when working with SMT solder because different tasks require different levels of precision. Fine-point tips are ideal for delicate jobs, allowing you to maneuver around tiny pads and leads with ease, while broader tips can handle larger connections more effectively. A well-chosen tip not only improves accuracy but also helps prevent overheating components—a common pitfall in PCB soldering that can lead to costly errors.
The Role of Solder Flux and Solder Paste
Solder flux plays an indispensable role in ensuring that your SMT solder flows smoothly and adheres properly to surfaces during PCB soldering. It helps clean oxidation off metal surfaces and improves the wetting properties of the solder, making it easier to achieve strong joints without cold solder connections. Similarly, using high-quality solder paste is crucial; it contains both flux and metal powder, allowing you to apply just the right amount of material directly onto pads before placing components—this combination ensures optimal performance in any surface mount technology project.
Preparing for PCB Soldering
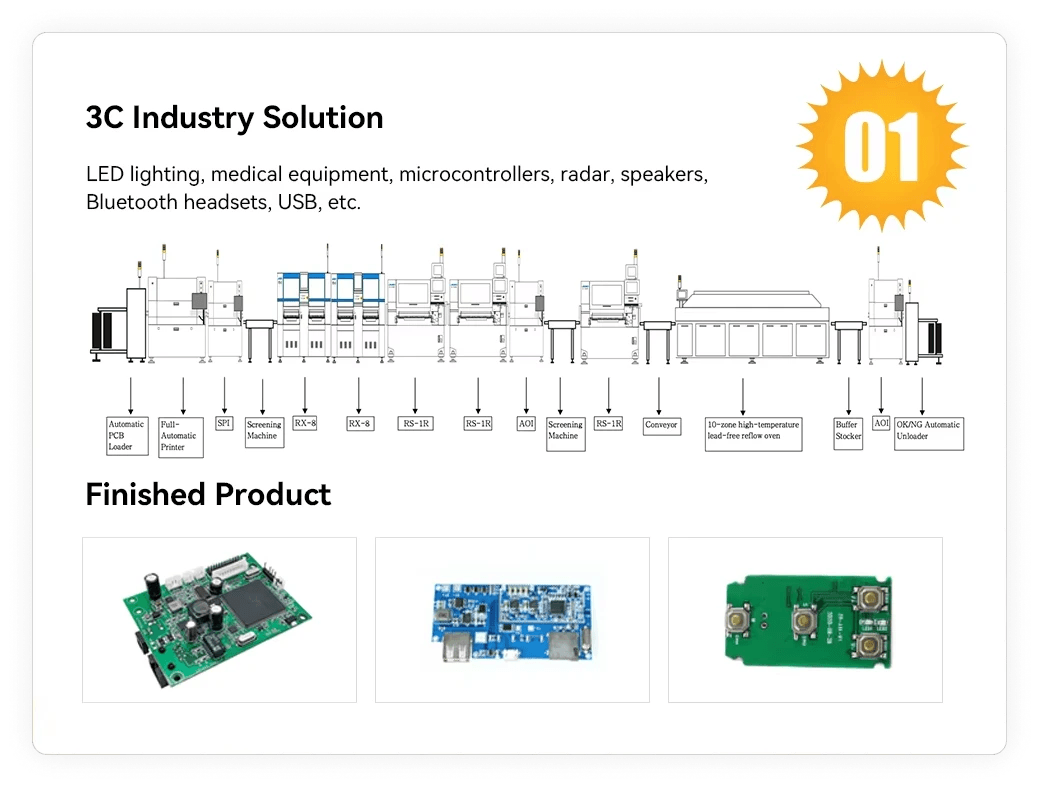
Before diving into the exciting world of PCB soldering, it’s crucial to lay the groundwork for a successful SMT (Surface-Mount Technology) project. This section will guide you through designing your layout, selecting the right solder for electronics, and following best practices for component placement. With these foundational steps in place, you'll be well on your way to mastering SMT soldering.
Designing Your Layout for SMT
Creating an effective layout is essential when working with SMT solder. Your design should prioritize space efficiency while ensuring that components are easily accessible during soldering. Additionally, consider the thermal management of your PCB; proper spacing can prevent overheating during the soldering process and improve overall performance.
When laying out your components, remember to account for the size and orientation of each part—especially when using smaller components that are common in SMT applications. Utilize software tools designed specifically for PCB design to visualize how everything fits together before committing to a physical prototype. A well-thought-out layout not only simplifies assembly but also enhances reliability in your final product.
Lastly, ensure that you incorporate adequate test points within your design to facilitate easier troubleshooting later on. This foresight can save you time and headaches down the line as you work with your PCB soldering tools and techniques.
Choosing the Right Solder for Electronics
Selecting the appropriate solder is vital in achieving optimal results in electronics assembly. For most SMT applications, lead-free solder is recommended due to its environmental benefits and compliance with international standards like RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances). However, traditional leaded solders are still popular among hobbyists due to their ease of use and superior flow characteristics.
When choosing between different types of solder paste or wire solders, consider factors such as melting point and alloy composition; these elements can significantly impact how well your smt solder performs during reflow or hand-soldering processes. It's also worth noting that certain solders may require specific fluxes—ensuring compatibility will help avoid issues like poor wetting or oxidation during application.
Ultimately, experimenting with various types of solders can lead you to discover which works best for your specific projects and preferences—a little trial-and-error never hurt anyone! Just remember: quality matters when it comes to achieving reliable connections on your PCBs.
Best Practices for Component Placement
Proper component placement is key to successful PCB assembly using SMT techniques. Start by positioning larger components first; this approach allows you more flexibility as you fill in gaps with smaller parts later on—think Tetris but with electronic bits! Additionally, pay attention to polarity markings on polarized components like capacitors or diodes; placing them incorrectly could lead to catastrophic failures down the line.
To enhance accuracy during placement, make use of tweezers or vacuum pick-up tools specifically designed for handling tiny surface-mount devices (SMDs). These handy gadgets will help ensure that each component is aligned perfectly before applying any smt solder or flux—no more fumbling around trying not to drop those minuscule resistors!
Finally, double-check each placement against your schematic before proceeding further; a quick inspection can save hours of frustration later if something goes awry during testing phases post-soldering. Following these best practices will set a solid foundation as you move into actual PCB soldering!
Step-by-Step SMT Soldering Process

Soldering surface-mount components can seem daunting at first, but with the right approach, it becomes a manageable task that opens up a world of possibilities in electronics. The key is to understand the nuances of SMT solder, solder flux, and solder paste while utilizing the appropriate soldering tools and tips for precision. Let’s dive into a detailed step-by-step guide that will help you master the art of PCB soldering.
Detailed Instructions for Soldering
To begin your SMT soldering journey, ensure that your workspace is clean and organized. Start by applying a small amount of solder paste onto each pad on the PCB where you'll be placing components; this will help the components adhere better during the heating process. Once you’ve placed your components on their respective pads, use your soldering iron to heat each joint carefully—just enough to melt the solder paste without creating cold joints or damaging sensitive parts.
Next, it’s essential to monitor how much heat you’re applying; too little won’t form a proper connection, while too much can damage both the component and PCB. A good practice is to hold your soldering iron tip against both the component lead and PCB pad simultaneously for just a second or two before adding more heat if necessary. After all connections are made, inspect each joint visually for quality—shiny and smooth joints indicate successful SMT soldering.
Heat Application Techniques
When working with SMT surface mount technology, mastering heat application techniques is crucial for successful results in PCB soldering. One effective method is using a hot air rework station; this allows you to evenly distribute heat across multiple joints simultaneously without direct contact from a tip. This technique is particularly beneficial when working with larger arrays of components or when desoldering parts that need replacement.
Another popular method involves using a fine-tipped soldering iron; this provides greater control over localized heating while minimizing risks associated with overheating adjacent components. It’s important to choose an appropriate temperature setting based on your specific type of solder for electronics; generally speaking, temperatures around 350°C are suitable for most lead-free solders but always refer to manufacturer specifications when in doubt. Remember that practice makes perfect—experiment with different techniques until you find what works best for your projects!
Avoiding Common Soldering Mistakes
Even seasoned professionals encounter pitfalls during SMT solder processes; however, being aware of common mistakes can save time and frustration down the line! One frequent error involves using too much or too little solder paste; excessive amounts can lead to bridging between pads while insufficient amounts may result in weak connections or cold joints—aim for just enough coverage on each pad without overflow!
Another mistake often seen in PCB soldering is improper placement of components before heating them up—always double-check orientation and alignment prior to applying heat since misaligned parts can cause significant issues later on! Lastly, don’t forget about cleaning up after yourself: residual flux from your work area can attract dust and debris which may interfere with future connections or overall performance—regularly clean surfaces using appropriate solvents designed specifically for electronic applications.
Quality Control in Soldering
Quality control in soldering is paramount to ensuring the longevity and reliability of electronic devices. The use of proper techniques and tools can significantly reduce defects, which is crucial when working with SMT solder and intricate PCB designs. By focusing on quality assurance, manufacturers can enhance their reputation and minimize costly rework.
Importance of Visual Inspection Systems
Visual inspection systems play a vital role in the quality control process for PCB soldering. These systems allow operators to catch potential issues before they escalate, ensuring that every joint made with solder paste is up to standard. With the right soldering tools, visual inspections can identify problems such as insufficient solder application or misaligned components early in the production line.
Incorporating advanced visual inspection technology also enhances the ability to detect defects that may not be visible to the naked eye. Automated systems equipped with high-resolution cameras and software algorithms can analyze each joint's integrity more effectively than manual inspections alone. This attention to detail helps maintain high standards for SMT surface mount technology applications, ultimately leading to more reliable electronics.
Testing for Reliability in PCB Soldering
Reliability testing is essential for confirming that SMT solder joints will withstand real-world conditions over time. Various methods such as thermal cycling tests, vibration tests, and humidity exposure assessments are employed to evaluate how well components hold up under stress. Utilizing appropriate solder flux during assembly can also improve joint strength by enhancing wetting properties during the reflow process.
Moreover, it’s critical to ensure that all components are adequately placed before testing begins; even minor misalignments can lead to catastrophic failures down the road. Regularly scheduled reliability tests not only highlight weaknesses but also provide insights into optimizing future designs and manufacturing processes involving solder for electronics applications. Ultimately, these practices contribute significantly toward achieving a robust final product.
Utilizing Bensun Technology for Quality Assurance
Bensun Technology has emerged as a leader in providing innovative solutions tailored specifically for quality assurance within PCB soldering processes. Their advanced tools integrate seamlessly into existing workflows, offering real-time monitoring capabilities that help ensure every aspect of SMT surface mount technology meets rigorous standards. By utilizing Bensun’s cutting-edge equipment, manufacturers gain access to unparalleled insights into their production lines.
The integration of smart technologies allows users to track key metrics related to both component placement accuracy and solder joint quality over time—data that proves invaluable when striving for excellence in manufacturing practices involving solder paste and flux usage. Additionally, Bensun's solutions facilitate quick identification of any deviations from established norms so corrective measures can be implemented promptly before they impact overall output quality.
This commitment to innovation not only enhances product reliability but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement within organizations focused on delivering exceptional electronics built using modern SMT techniques.
Conclusion
In wrapping up our exploration of SMT soldering, it's clear that mastering this art is essential for anyone looking to thrive in the world of modern electronics. The precision and efficiency offered by SMT surface mount technology can significantly enhance your PCB soldering projects, making them more reliable and efficient. With the right tools, techniques, and a sprinkle of practice, you can elevate your soldering skills to new heights.
Mastering the Art of SMT Solder
To truly master the art of SMT solder, a deep understanding of solder flux and solder paste is crucial. These materials not only aid in achieving clean joints but also ensure that your components are securely attached to the PCB. By honing your skills with various soldering tools and applying expert soldering tips, you'll find yourself producing professional-quality results in no time.
Resources for Further Learning
For those eager to continue their journey into the world of electronics, numerous resources are available that delve deeper into SMT technology and PCB soldering techniques. Online forums, instructional videos, and comprehensive guides can provide invaluable insights into advanced methods and troubleshooting strategies. Additionally, consider joining local maker spaces or workshops where you can share knowledge with fellow enthusiasts and refine your skills hands-on.
Innovations in Surface-Mount Technology
The landscape of surface-mount technology is ever-evolving, with innovations continually reshaping how we approach electronics assembly. New developments in solder for electronics are enhancing reliability while reducing production costs—an exciting prospect for hobbyists and professionals alike! Staying informed about these advancements will not only keep your skills sharp but also inspire fresh ideas for future projects.
