Introduction

In the realm of electrical distribution, feeder systems serve as the backbone, channeling power to various components and ensuring efficient operation. These systems are crucial for maintaining the reliability and functionality of electric machines, including advanced technologies like pick and place machines. Understanding feeder systems is essential for optimizing performance in manufacturing environments that utilize SMT (Surface Mount Technology) machines.
Understanding Feeder Systems in Electrical Distribution
Feeder systems are designed to transport electrical energy from substations to consumers or specific machinery, such as SMT electric feeders that supply power to pick & place machines. Each type of feeder system—whether radial, loop, or network—has its unique characteristics tailored for different applications in electrical distribution. By grasping these distinctions, manufacturers can make informed decisions about the most effective setups for their operations.
Importance of Proper Feeder Systems
Choosing the right feeder system is critical not just for efficiency but also for safety and reliability in operations involving machine SMT technology. An inadequate feeder can lead to power losses or equipment failures, which may disrupt production processes involving electric machines like pick and place machines. Therefore, a well-designed feeder system enhances overall productivity while minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
Overview of Feeder Types
There are three primary types of feeder systems: radial, loop, and network feeders—each serving distinct purposes within electrical distribution networks. Radial feeders offer simplicity but can be vulnerable to outages; loop feeders provide redundancy; while network feeders allow for maximum flexibility and reliability in complex setups like those found with SMT machines. Understanding these types will help businesses optimize their use of SMT electric feeders alongside other essential machinery in their production lines.
Types of Feeder Systems

In the realm of electrical distribution, feeder systems serve as the backbone for efficient power delivery. Understanding the different types of feeder systems is crucial for optimizing performance in various applications, including those involving SMT machines and electric machines. This section will delve into three primary types: Radial, Loop, and Network feeder systems.
Radial Feeder Systems
Radial feeder systems are characterized by a single source feeding multiple loads along a straight line. This setup is commonly found in smaller electrical networks where simplicity and cost-effectiveness take precedence. However, while radial systems are easy to design and install, they can suffer from reliability issues; if there’s a fault at any point along the line, all downstream loads lose power.
For SMT electric feeders, this means that if one machine pick and place encounters an issue, it could halt production for all connected devices. Despite these drawbacks, radial feeder systems are widely used due to their straightforward configuration and low maintenance requirements. They are ideal for applications where redundancy isn’t critical but operational costs need to be minimized.
Loop Feeder Systems
Loop feeder systems offer a more resilient alternative by connecting loads in a circular manner back to the source. This configuration allows electricity to flow through two paths; hence if one path fails due to an issue with an electric machine or pick & place machine, power can still reach other devices through the alternate route. This enhances reliability significantly compared to radial feeders.
The benefits of using loop feeders extend beyond just reliability; they also allow for maintenance without interrupting service to connected SMT machines or other equipment. In scenarios where continuous operation is vital—like in manufacturing lines utilizing advanced SMT technology—loop feeders shine as an optimal choice. Real-world implementations show that industries leveraging loop configurations enjoy decreased downtime and improved productivity.
Network Feeder Systems
Network feeder systems represent the most complex type among these three categories but come with substantial advantages in terms of flexibility and reliability. These systems interconnect multiple sources with various paths leading to loads, allowing them to share power dynamically based on demand fluctuations across different electric machines or SMT setups like pick and place machines.
Choosing a network feeder often involves considering factors such as load diversity and future expansion needs within manufacturing environments using machine SMT technology. The ability of network feeders to reroute electricity during faults ensures minimal disruption—a key advantage when operating sophisticated SMT machines requiring constant uptime for efficiency gains. Case studies indicate that businesses adopting network configurations see significant improvements in operational resilience and overall system performance.
Radial Feeder Systems Explained
Radial feeder systems are one of the most straightforward designs in electrical distribution networks. They consist of a single power source that branches out to various loads, resembling the spokes of a wheel. This simplicity makes radial systems easy to understand and implement, but they come with their own set of pros and cons.
Characteristics of Radial Systems
Radial systems are characterized by their unidirectional flow of electricity from a single source to multiple endpoints. This means that if one branch experiences an issue, it can disrupt service to all downstream loads connected to that branch. In the context of SMT electric feeders, this design can impact the performance and reliability of machines like pick and place machines if not properly managed.
The radial configuration often utilizes fuses or circuit breakers at each branch point for protection, ensuring that faults can be isolated effectively. Additionally, radial feeders typically require less infrastructure compared to more complex systems like loops or networks, making them cost-effective for certain applications. However, their vulnerability during outages highlights the importance of redundancy in critical operations involving SMT machines.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages of radial feeder systems include ease of installation and maintenance due to their simple design structure. They are generally less expensive than other types because they require fewer components and less wiring—ideal for smaller operations using SMT electric feeders where budget constraints might be a concern. Furthermore, troubleshooting is relatively straightforward since issues can usually be traced back along a single path.
On the downside, radial systems suffer from reliability issues; if there is a fault on one feeder line, it can lead to significant downtime for connected devices such as machine pick and place setups. Additionally, without backup feeds or alternative routing options in place, any disturbance in power supply could halt production entirely—something no manufacturer wants when relying on efficient SMT machines for assembly tasks.
Applications in Electrical Distribution
Radial feeder systems find widespread application across various sectors due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. They are commonly used in residential areas where loads are predictable and manageable without requiring complex configurations—perfect for small-scale setups utilizing SMT electric feeders for basic manufacturing needs like electronics assembly with pick & place machines.
In industrial settings, radial feeders may serve specific zones within larger facilities where dedicated power feeds ensure consistent operation without overloading circuits tied into more extensive networks. Although not ideal for every situation—especially where high reliability is paramount—they remain an effective choice when paired with robust machinery capable of handling potential disruptions inherent in this type of system.
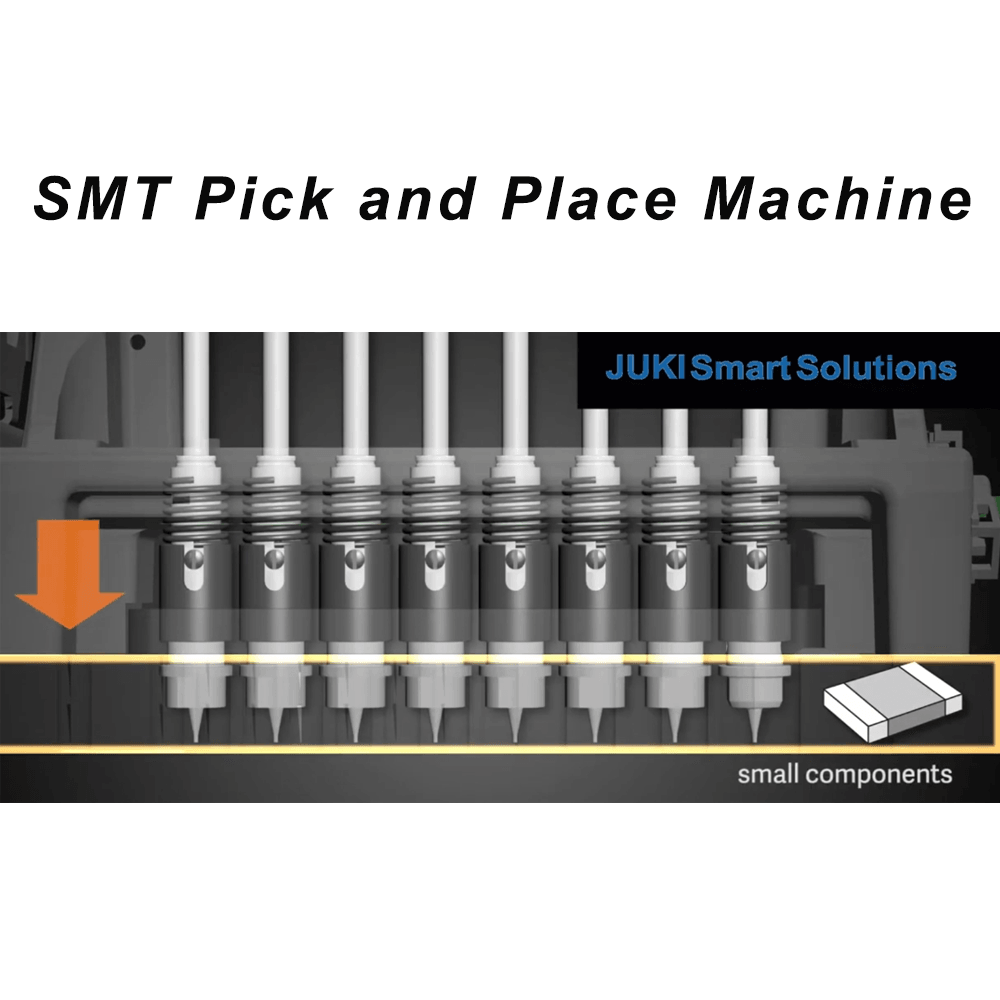
Loop Feeder Systems Explained
Loop feeder systems are a fascinating approach to electrical distribution, designed to enhance reliability and efficiency. By forming a loop, these systems provide multiple paths for electricity to flow, ensuring that if one path fails, the power can still reach its destination through another route. This redundancy is particularly valuable in environments where consistent power supply is critical.
Features of Loop Systems
Loop systems boast several distinctive features that set them apart from traditional feeder configurations. One of the primary characteristics is their interconnected network of feeders that allows for flexibility in power distribution. In addition, loop feeders can be equipped with smart technology to monitor performance and detect faults in real-time, which is essential when integrating with advanced equipment like SMT machines or pick and place machines.
Another notable feature is the ability to balance loads effectively across the looped structure, optimizing energy use and minimizing wastage. This load-balancing capability ensures that electric machines operate efficiently without overloading any single component of the system. Furthermore, loop feeder systems can be designed to accommodate future expansions or modifications easily, making them ideal for growing manufacturing environments.
Benefits of Using Loop Feeders
The advantages of using loop feeders are numerous and impactful on overall system performance. First and foremost, they significantly improve reliability by providing alternative pathways for electricity; this means that even if one section experiences an outage or maintenance issue, other paths can continue supplying power without interruption. For industries reliant on SMT electric feeders and machine pick and place operations, this reliability translates directly into increased productivity.
Moreover, loop feeder systems often lead to reduced operational costs over time due to their efficiency in energy distribution and lower maintenance needs compared to radial systems. The enhanced monitoring capabilities also allow for proactive maintenance strategies rather than reactive ones—resulting in fewer unexpected downtimes for SMT machines and associated equipment like pick & place machines.
Lastly, these systems support scalability within manufacturing facilities by allowing easy integration with additional electric machines as production demands grow. As new technologies emerge or existing processes evolve, manufacturers can adapt their electrical infrastructure seamlessly without significant overhaul costs or downtime.
Real-world Examples
Real-world applications of loop feeder systems highlight their effectiveness across various industries. For instance, a leading electronics manufacturer implemented a loop feeder system within its assembly line where SMT electric feeders were crucial for operations involving multiple pick & place machines working simultaneously on circuit board assemblies. The result was not only enhanced uptime but also improved throughput rates as workers could rely on uninterrupted power supply even during peak production hours.
Another example comes from an automotive plant where electric machine integration demanded robust electrical infrastructure capable of handling high currents while maintaining safety standards throughout production processes. By utilizing a networked loop system approach combined with advanced monitoring tools tailored specifically for machine SMT applications, the plant saw significant reductions in both energy consumption and operational risks associated with electrical failures.
These examples illustrate how adopting loop feeder systems has become synonymous with modernization efforts in manufacturing settings—creating environments where efficiency thrives alongside innovation.
Network Feeder Systems Explained

Network feeder systems are an essential component of modern electrical distribution, designed to enhance reliability and efficiency. These systems utilize interconnected pathways to deliver power, ensuring that if one route encounters a problem, alternative routes can maintain service continuity. This redundancy makes network feeders particularly valuable in environments that demand high availability, such as manufacturing plants using SMT machines.
Understanding Network Topologies
Network topologies refer to the arrangement of various elements (links, nodes) in a communication or electrical system. In the context of network feeder systems, common topologies include ring and mesh configurations, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. For instance, a ring topology connects various points in a circular manner, while a mesh topology interlinks multiple nodes for maximum redundancy—ideal for applications involving electric machines where uptime is critical.
Why Choose a Network Feeder?
Choosing a network feeder system comes with several compelling advantages. First and foremost is reliability; these systems minimize downtime by allowing power rerouting in case of faults—perfect for operations that rely on machine pick and place technology. Additionally, network feeders offer scalability; as manufacturing needs grow or change (like integrating new SMT electric feeders), these systems can adapt without major overhauls.
Case Studies in Implementation
Examining real-world implementations of network feeder systems reveals their transformative impact on productivity. For example, one electronics manufacturer upgraded their infrastructure to include advanced pick & place machines connected via a robust network feeder system. This change led to an impressive 30% increase in operational efficiency due to reduced downtime and enhanced flexibility in managing their SMT machines.
The Role of SMT Electric Feeders
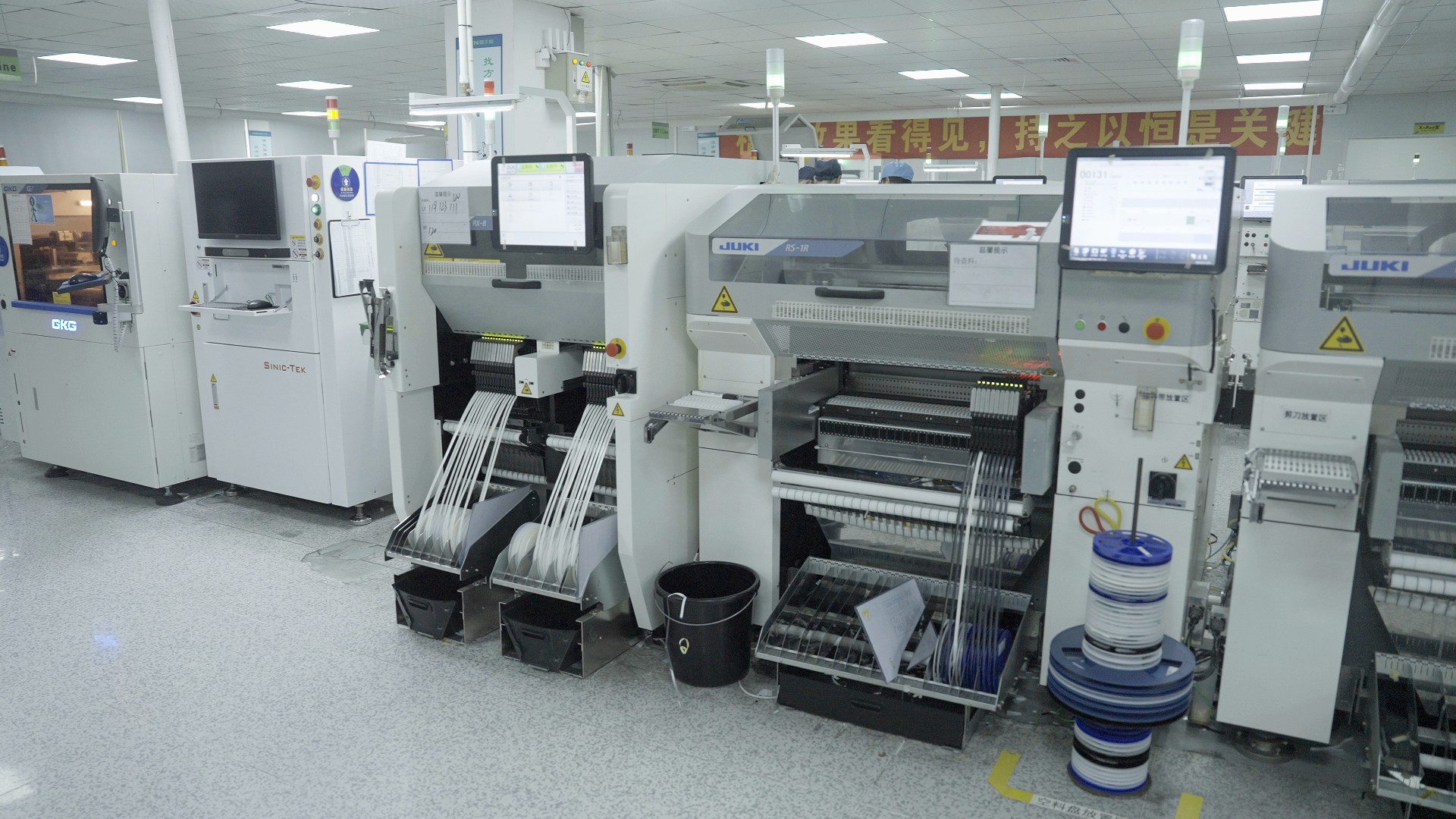

In the realm of modern manufacturing, SMT electric feeders play a crucial role in streamlining production processes. These specialized devices are integral to the operation of various SMT machines, particularly in the context of pick and place machines. By ensuring a continuous supply of components, SMT electric feeders enhance overall efficiency and productivity on the factory floor.
Importance of SMT Electric Feeders in Manufacturing
SMT electric feeders are essential for maintaining the flow of materials in high-speed assembly lines. Without these feeders, machine pick and place operations would face significant delays due to manual loading or component shortages. Their ability to automatically feed components ensures that production runs smoothly, reducing downtime and increasing output.
In addition to improving operational efficiency, SMT electric feeders also contribute to quality control within manufacturing processes. By providing precise amounts of components at just the right time, they minimize the risk of errors that can occur during manual handling. This reliability is vital for industries where precision is paramount, such as electronics manufacturing.
Integration with Electric Machines
The integration of SMT electric feeders with electric machines marks a significant advancement in automation technology. These systems work seamlessly together; as an electric machine performs its tasks—like placing components on a circuit board—the feeder supplies necessary parts without interruption. This harmonious relationship allows for faster production cycles and enhanced responsiveness to changing demands.
Moreover, modern pick & place machines are designed with compatibility in mind, making it easier than ever to integrate various types of SMT electric feeders into existing setups. This flexibility means manufacturers can customize their assembly lines according to specific needs without overhauling their entire system. Such adaptability is key in today’s fast-paced market where speed and precision matter most.
How SMT Machines Enhance Efficiency
SMT machines equipped with advanced pick and place capabilities significantly boost manufacturing efficiency by leveraging state-of-the-art technology alongside reliable SMT electric feeders. These machines not only handle components quickly but also do so with remarkable accuracy—ensuring every piece lands precisely where it should be on a circuit board or other assembly area.
Furthermore, integrating smart technologies into these systems allows for real-time monitoring and adjustments during production runs; this means any potential issues can be addressed before they escalate into costly problems. The combination of effective machine smt operations with high-performance feeders results in optimized workflows that save time and reduce waste across all stages of production.
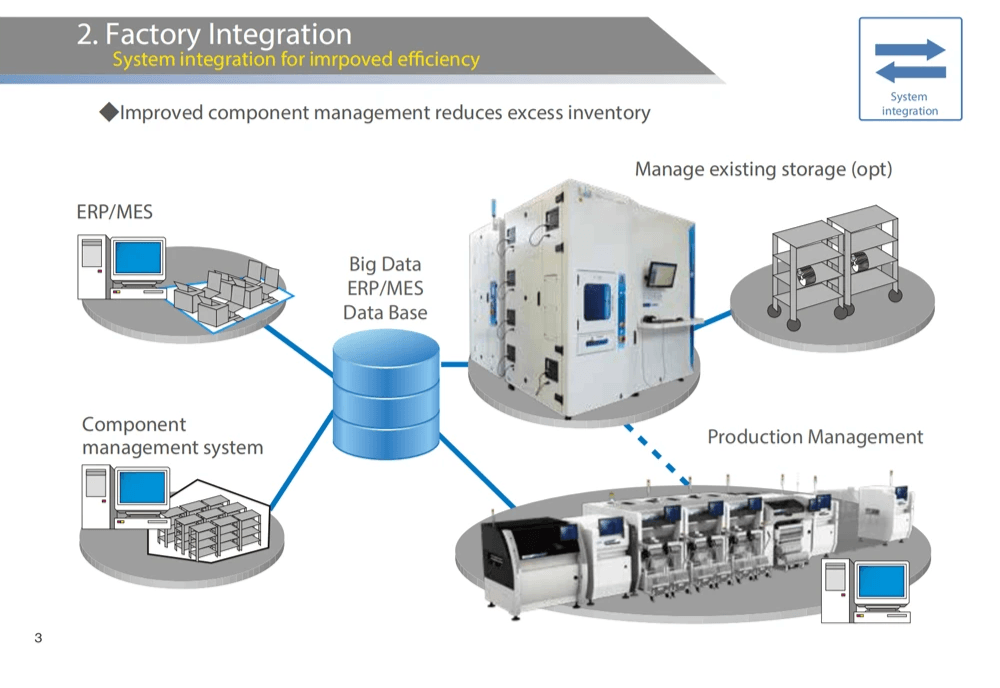
Bensun Technology and Feeder Systems

Bensun Technology has carved a niche in the realm of feeder systems, particularly for SMT (Surface Mount Technology) applications. By offering a suite of services tailored to enhance the performance of SMT machines, Bensun ensures that electric machines operate at peak efficiency. Their commitment to innovation positions them as a go-to provider for businesses looking to optimize their manufacturing processes.
Overview of Bensun Technology Services
Bensun Technology provides an array of services focused on improving the functionality and reliability of SMT electric feeders. These services range from consultation on feeder system design to implementation support for advanced pick and place machines. By leveraging cutting-edge technology, Bensun enables manufacturers to maximize productivity while minimizing downtime associated with machine malfunctions.
The company emphasizes the integration of its services with existing electric machines, ensuring seamless compatibility across various platforms. This approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also allows companies to adapt quickly to changing production demands. With a strong focus on customer satisfaction, Bensun tailors its offerings based on specific needs within the realm of machine SMT applications.
Impact on SMT Machine Performance
The performance of SMT machines is significantly influenced by the quality and design of the smt electric feeder systems they utilize. A well-designed feeder can dramatically improve the speed and accuracy with which components are placed during assembly processes, making it integral to any pick & place machine operation. When these feeders are optimized by Bensun’s expertise, manufacturers experience reduced cycle times and enhanced throughput.
Moreover, integrating high-performance feeders with electric machines leads to fewer errors in component placement—an essential factor in maintaining product quality standards. As a result, businesses can achieve higher yield rates while also minimizing material waste associated with improper placements or machine failures. The synergy between advanced smt electric feeders and innovative technology solutions provided by Bensun truly elevates overall machine performance.
Custom Solutions for Feeder Systems
Understanding that no two manufacturing environments are identical, Bensun Technology excels at providing custom solutions tailored specifically for each client's needs regarding feeder systems. Whether it's designing specialized smt electric feeders or optimizing existing setups for enhanced efficiency, their team focuses on delivering results that meet precise operational requirements. This customization extends beyond mere hardware; it encompasses software integration that facilitates smoother interactions between various components within machine pick and place operations.
Bensun's ability to create bespoke solutions means clients can enjoy increased flexibility in their production lines while still benefiting from robust support structures provided by experienced technicians. Additionally, these custom solutions often lead to long-term cost savings due to improved machinery longevity and reduced maintenance needs over time—an attractive proposition for any manufacturer reliant on reliable pick & place machinery.
In summary, partnering with Bensun Technology not only streamlines your feeding operations but also transforms how you approach your entire manufacturing process through tailored innovations designed specifically around your unique challenges.
Conclusion
In wrapping up our exploration of feeder systems, it’s clear that understanding the nuances of each type is essential for optimizing electrical distribution. From radial to network systems, each configuration offers unique advantages tailored to specific applications. Moreover, the integration of SMT electric feeders with machines like pick and place machines highlights the importance of innovation in improving manufacturing efficiency.
Key Takeaways on Feeder Systems
Feeder systems are pivotal in ensuring reliable power distribution across various applications, especially in manufacturing settings utilizing advanced technology like SMT machines. Radial feeder systems provide simplicity and cost-effectiveness, while loop and network systems enhance reliability and redundancy. Ultimately, choosing the right system can significantly impact operational efficiency and machine performance.
Importance of Choosing the Right System
Selecting an appropriate feeder system is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of electric machines, including pick and place machines used in SMT processes. The right choice can lead to improved uptime and reduced maintenance costs while ensuring seamless integration with existing infrastructure. As industries evolve, aligning feeder solutions with specific operational needs becomes increasingly vital for sustained success.
Future Trends in Electrical Distribution Systems
The future of electrical distribution is leaning towards smarter technologies that incorporate real-time data analytics to optimize performance continuously. Innovations such as enhanced SMT electric feeders will likely play a significant role in supporting advanced manufacturing techniques like machine pick and place operations. As we move forward, integrating sustainability into these systems will also be paramount, driving advancements that prioritize energy efficiency alongside productivity.
