Introduction

In the world of electronics manufacturing, selective soldering has emerged as a game-changer. This specialized process allows for precise soldering of specific components on a printed circuit board (PCB), ensuring both efficiency and quality. With advancements in technology, selective soldering machines have become indispensable tools in modern PCB assembly.
Understanding Selective Soldering Machines
Selective soldering machines are designed to apply solder and flux only where needed, minimizing waste and maximizing accuracy. Unlike traditional wave soldering, which submerges entire boards in molten solder, selective soldering focuses on targeted areas, making it ideal for complex assemblies with mixed technologies. These machines utilize a variety of techniques to deliver consistent results, ensuring that every joint is reliable and robust.
The Importance of Solder and Flux
Solder and flux play critical roles in the effectiveness of any soldering process, including station soldering. Solder is the metal alloy that creates electrical connections between components, while flux cleans and prepares surfaces for optimal adhesion. Choosing the right types of solder and flux is essential; improper application can lead to weak joints or even component failure.
Benefits of Using a Soldering Machine
Investing in quality soldering equipment offers numerous advantages for manufacturers looking to enhance productivity and product reliability. A well-designed solder machine not only improves precision but also reduces human error during assembly processes. Furthermore, features like advanced temperature control and automated flux application ensure that each PCB meets high standards without compromising speed or efficiency.
What is Selective Soldering?
Selective soldering is a specialized process in the world of PCB assembly that focuses on precisely applying solder and flux to specific areas of a printed circuit board (PCB). This method allows for targeted soldering, which is particularly beneficial for complex assemblies with sensitive components. By using a soldering machine designed for selective applications, manufacturers can achieve high-quality connections without the risk of damaging adjacent parts.
Definition and Process Overview
At its core, selective soldering involves the use of a solder pot to melt solder and apply it directly to designated areas on a PCB while avoiding unintended contact with other components. The process typically starts with the application of flux, which helps improve wetting and adhesion between the solder and the surfaces being joined. Once the flux is applied, the molten solder flows into place through various techniques like dip or spray methods, ensuring efficient and accurate connections.
This precision makes selective soldering an attractive alternative for manufacturers who need reliable results without compromising quality. Unlike traditional methods that may require more extensive setups or lead to excess waste, this approach minimizes both material usage and time spent on each assembly. As such, it’s become a go-to choice for many in need of effective station soldering solutions.
Key Components of Selective Soldering
The key components that make up a selective soldering system include the solder pot, flux applicator, and various nozzles or pumps designed to control the flow of molten solder. The solder pot holds the liquid metal at an optimal temperature while allowing operators to manage its application accurately. Meanwhile, advanced flux applicators ensure that only necessary areas receive treatment before being joined by molten metal.
In addition to these core elements, modern selective soldering machines often feature programmable settings for repeatable results across multiple production runs. This automation not only enhances efficiency but also reduces human error during assembly processes—making it easier than ever to produce high-quality PCBs consistently. Understanding these components helps businesses choose the best equipment tailored to their specific needs.
Comparison with Wave Soldering
When comparing selective soldering with wave soldering, several distinctions emerge that highlight their respective advantages and disadvantages in PCB manufacturing processes. Wave soldering involves passing an entire board over a wave of molten solder; this technique is efficient for large volumes but can lead to issues like bridging or excessive heat exposure on sensitive components. In contrast, selective soldering targets only specific joints using precise application methods—resulting in less thermal stress overall.
Moreover, while wave soldering may be suitable for simpler designs with fewer complex parts or through-hole connections, selective methods shine when dealing with intricate layouts featuring surface-mount devices (SMDs) or mixed technologies where careful handling is crucial. Ultimately, choosing between these two approaches depends largely on production volume requirements as well as component sensitivity—making it essential for manufacturers to understand their options thoroughly before investing in equipment.
The Role of Solder and Flux in PCB Assembly
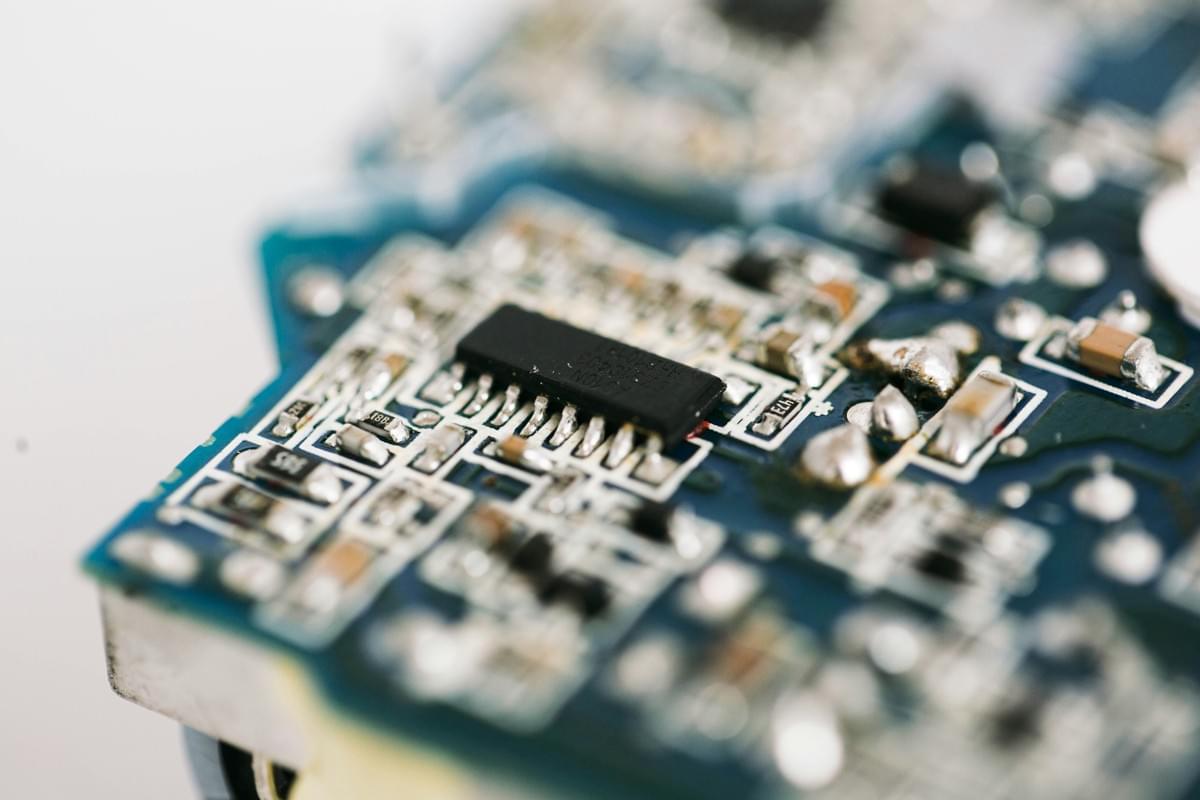
In the world of PCB assembly, solder and flux play pivotal roles that can make or break the quality of your final product. Understanding their significance is crucial, especially when using a soldering machine for selective soldering processes. This section delves into the types of solder and flux used, their proper application, and how they ultimately affect the quality of your assembly.
Types of Solder and Flux Used
When it comes to selective soldering, there are various types of solder that you can choose from, each designed for specific applications. Lead-based solders have been traditional favorites due to their excellent wetting properties; however, with increasing environmental regulations, lead-free options like SAC (Tin-Silver-Copper) alloys have gained popularity. On the flip side, fluxes come in different forms such as rosin-based or water-soluble varieties—each serving to enhance the soldering process by preventing oxidation and improving adhesion.
Flux is just as vital as solder itself; it prepares surfaces for bonding by removing oxides and contaminants. In station soldering setups, choosing the right combination of solder & flux can significantly influence both efficiency and effectiveness during assembly. Selecting high-quality materials ensures a reliable connection while minimizing defects in your PCBs.
Importance of Proper Application
The application method for both solder and flux is critical in achieving optimal results during selective soldering. Applying too much or too little can lead to issues such as cold joints or excessive bridging between components—both nightmares for any PCB manufacturer! Therefore, understanding how to effectively use a solder pot in conjunction with your chosen materials is essential for maintaining high-quality standards.
Proper application techniques also contribute to better thermal management during the soldering process. With careful consideration given to temperature settings on your best soldering equipment, you can ensure that both the flux activates properly and that the molten solder flows where it's needed most without damaging sensitive components. Mastery over these techniques will not only improve yields but also enhance overall production efficiency.
How Solder and Flux Affect Quality
The relationship between quality control in PCB assembly and the use of appropriate solder & flux cannot be overstated. High-quality materials result in strong electrical connections while reducing defects that could lead to product failure down the line—an expensive oversight! In contrast, inferior materials may compromise performance even if everything else appears perfect on paper.
Furthermore, improper interaction between selected solders and fluxes can lead to corrosion or other long-term reliability issues that are difficult to detect initially but become problematic later on. Regular testing during development phases helps ensure compatibility among all components involved in wave soldering versus selective methods—a crucial step if you're aiming for long-lasting products!
In summary, understanding how different types of solders work together with various fluxes—and applying them correctly—is key to achieving high-quality outcomes in PCB assembly processes like selective soldering.
Choosing the Best Selective Soldering Equipment
When it comes to selective soldering, choosing the right equipment can make all the difference between a smooth operation and a frustrating experience. With various options available, it's essential to identify features that align with your specific needs for solder and flux application. A well-chosen soldering machine can enhance productivity, improve quality, and ultimately save costs in your PCB assembly process.
Features to Look for in a Soldering Machine
When selecting the best soldering equipment, several key features should be on your checklist. First, look for precision control systems that allow you to adjust temperature and flow rates accurately; this ensures optimal solder and flux application tailored to different components. Additionally, consider machines equipped with advanced solder pot designs that facilitate easy maintenance and consistent performance during station soldering tasks.
Another important feature is automation capabilities; automated systems can significantly reduce human error while increasing throughput. Furthermore, ensure that the machine supports various types of solder & flux materials since versatility is crucial for adapting to different projects or production runs. Lastly, user-friendly interfaces make it easier for operators to navigate settings quickly—saving time and minimizing mistakes during critical operations.
Brands to Consider: Bensun Technology's Offerings
Bensun Technology stands out as a reputable name in the world of selective soldering equipment, offering a range of machines tailored for diverse manufacturing needs. Their products are known for high reliability and innovative features designed specifically for efficient use of solder & flux in PCB assembly processes. Whether you're looking for entry-level models or advanced systems with automation capabilities, Bensun has something that fits every budget.
One notable offering from Bensun is their state-of-the-art selective soldering machine equipped with customizable parameters that allow users to achieve precise results consistently. These machines also come with robust support services ensuring you have assistance whenever needed—making them an excellent choice for both newcomers and seasoned professionals alike. Investing in Bensun technology means investing in quality; their commitment to excellence makes them a trusted partner in selective soldering solutions.
Evaluating Equipment for Your Needs
Before making a purchase decision on selective soldering equipment, it's essential to evaluate how well each option meets your specific requirements. Start by assessing your production volume; higher throughput may necessitate more advanced machinery capable of handling increased workload efficiently without compromising quality or speed during wave soldering processes.
Next, consider the types of components you'll be working with; some machines excel at handling intricate designs while others are better suited for larger parts—matching equipment capability with project demands is crucial here! Finally, don't forget about after-sales support; reliable service can save you headaches down the road if issues arise during operation or maintenance becomes necessary.
Best Practices for Station Soldering

When it comes to maximizing the efficiency and quality of your station soldering, following best practices is essential. Proper preparation, technique, and maintenance can significantly impact the performance of your soldering machine and the overall success of your selective soldering process. Let's dive into some key areas to ensure you're getting the most out of your equipment.
Preparing Your PCB for Soldering
Before you even think about applying solder and flux, it's crucial to prepare your PCB thoroughly. Start by cleaning the surface to remove any contaminants that could interfere with adhesion; a clean surface is a happy surface! Additionally, make sure all components are properly aligned and securely placed on the board—this will help prevent any mishaps during the solder application process.
Another important step in preparation is to inspect for any damage or defects on both the PCB and components. Any issues found should be addressed prior to soldering; after all, you wouldn’t want a rogue wave (solder) ruining your masterpiece! Lastly, ensure that you have all necessary tools at hand—having everything ready saves time and reduces stress during station soldering.
Techniques for Effective Solder Application
Now that you've prepped like a pro, let’s talk about techniques for effective solder application with your best soldering equipment. One key aspect is controlling temperature; too hot can lead to component damage while too cool might not create strong joints. Using a well-calibrated solder pot is vital here—temperature stability ensures optimal results across each joint.
Another technique worth mastering involves applying just the right amount of solder & flux during selective soldering. Too much can create messy blobs while too little may result in weak connections; finding that sweet spot takes practice but pays off in quality assurance! Finally, don’t forget about timing; allowing sufficient dwell time when applying heat will help achieve proper melting without overheating components.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
To keep your station soldering setup running smoothly over time, regular maintenance is non-negotiable! Start by routinely cleaning your solder pot as residue buildup can affect performance during selective soldering operations—nobody wants an unreliable machine when deadlines loom large! Regularly check nozzles and tips for wear or clogs as well; these small parts play a big role in ensuring precision application of solder & flux.
Additionally, always follow manufacturer guidelines regarding maintenance schedules for both equipment and consumables like fluxes or solders used in wave soldering processes. Keeping up with these recommendations will extend the life of your best soldering equipment significantly! Lastly, don’t overlook software updates if applicable; advancements often include improvements that enhance functionality or address known issues.
Innovations in Selective Soldering Technology

The world of selective soldering is evolving at a rapid pace, driven by technological advancements that enhance efficiency and quality. Innovations in solder and flux applications are streamlining processes, making them faster and more reliable than ever before. As manufacturers embrace these changes, the landscape of PCB assembly continues to transform, setting new standards for excellence.
Advancements in Solder Pot Design
Modern solder pots are being reimagined to improve temperature control and reduce waste, which is crucial for effective selective soldering. These advancements ensure that the solder and flux maintain optimal performance throughout the assembly process while minimizing oxidation and contamination risks. With improved designs, manufacturers can achieve more precise application of solder & flux, resulting in higher-quality connections on PCBs.
Furthermore, today's solder pots often feature enhanced heating elements that allow for quicker heat-up times and better thermal stability. This means less downtime during production runs, ultimately leading to increased output without sacrificing quality. The latest innovations also include user-friendly interfaces that simplify monitoring and adjustments during station soldering operations.
Automation in Selective Soldering Systems
Automation is revolutionizing selective soldering systems by integrating sophisticated robotics into the process, allowing for precision placement of components with minimal human intervention. This shift not only improves consistency but also significantly reduces labor costs associated with manual soldering tasks. Automated systems can precisely control the application of solder & flux, ensuring optimal results every time.
Moreover, automated selective soldering machines are equipped with advanced vision systems that detect component alignment issues before they become problematic. This capability enhances overall production reliability while reducing scrap rates due to misalignment or poor connections from traditional wave soldering methods. As automation continues to advance, manufacturers will find themselves leveraging these technologies to stay competitive in a fast-paced market.
The Future of PCB Manufacturing
Looking ahead, the future of PCB manufacturing appears bright as innovations in selective soldering pave the way for smarter production techniques. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into these systems promises even greater efficiency through predictive maintenance and real-time process adjustments based on data analytics. This level of sophistication will allow manufacturers to optimize their use of best soldering equipment while minimizing material waste.
Additionally, as sustainability becomes an increasing priority across industries, eco-friendly materials for solders and fluxes are likely to gain traction within selective soldering applications. By focusing on greener alternatives without compromising performance or reliability, companies can meet consumer demand while adhering to environmental regulations effectively. Ultimately, these innovations will shape a new era for PCB manufacturing where quality meets sustainability head-on.
Conclusion
In summary, selective soldering stands out as a highly efficient method for PCB assembly, offering precision and reliability that other methods, like wave soldering, simply can't match. The strategic use of solder and flux is crucial in this process, ensuring strong connections while minimizing the risk of defects. By investing in the best soldering equipment available, manufacturers can enhance their production quality and operational efficiency.
Recap of Selective Soldering Benefits
Selective soldering delivers numerous advantages that make it an attractive option for many businesses involved in electronics manufacturing. This technique allows for targeted application of solder and flux, which reduces waste and improves overall quality by preventing excess material from causing shorts or cold joints. Furthermore, selective soldering machines are designed to handle complex assemblies with varying component heights and orientations seamlessly.
Why Invest in Quality Soldering Equipment
Investing in quality soldering equipment is essential for achieving optimal results in any PCB assembly process. High-quality machines not only provide better control over the application of solder & flux but also ensure longevity and reliability in production runs. Additionally, top-tier equipment often comes with advanced features such as automated processes and superior solder pot designs that enhance productivity while reducing labor costs.
Choosing the Right Partner for Your Needs
Selecting the right partner for your selective soldering needs can significantly impact your business's success. Look for manufacturers who offer comprehensive support services alongside their best soldering equipment to ensure you have assistance when needed. Collaborating with a trusted provider not only guarantees access to high-quality machines but also fosters long-term relationships that can lead to innovations tailored specifically for your station soldering requirements.
